# AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda (opens new window) is a scalable compute service that allows you to execute code without provisioning or managing servers. You can use AWS Lambda to build a variety of real-time serverless data processing systems quickly and easily. You must connect AWS Lambda to Workato using one of the following methods:
- IAM user access key authentication
- IAM role authentication
LEGACY ACCESS KEY AUTHENTICATION
Access key authentication is a legacy authentication format. We highly recommend using IAM role authentication.
# Connect to AWS Lambda using IAM user access key
Note that using an IAM user access key to connect to AWS Lambda is allowed but deprecated. You must provide the user credentials (opens new window) for this authentication method.
# Input fields for access key
- Fields for access key authentication.
- Connection name
- Give this connection a unique name that identifies which AWS Lambda instance it is connected to.
- Location
- The Workato project that requires the connection.
- Authorization type
- Select Access Key.
- Access key ID
- The ID of the user.
- Secret access key
- The secret of the user.
- Region
- Provide the region for this AWS Lambda account.
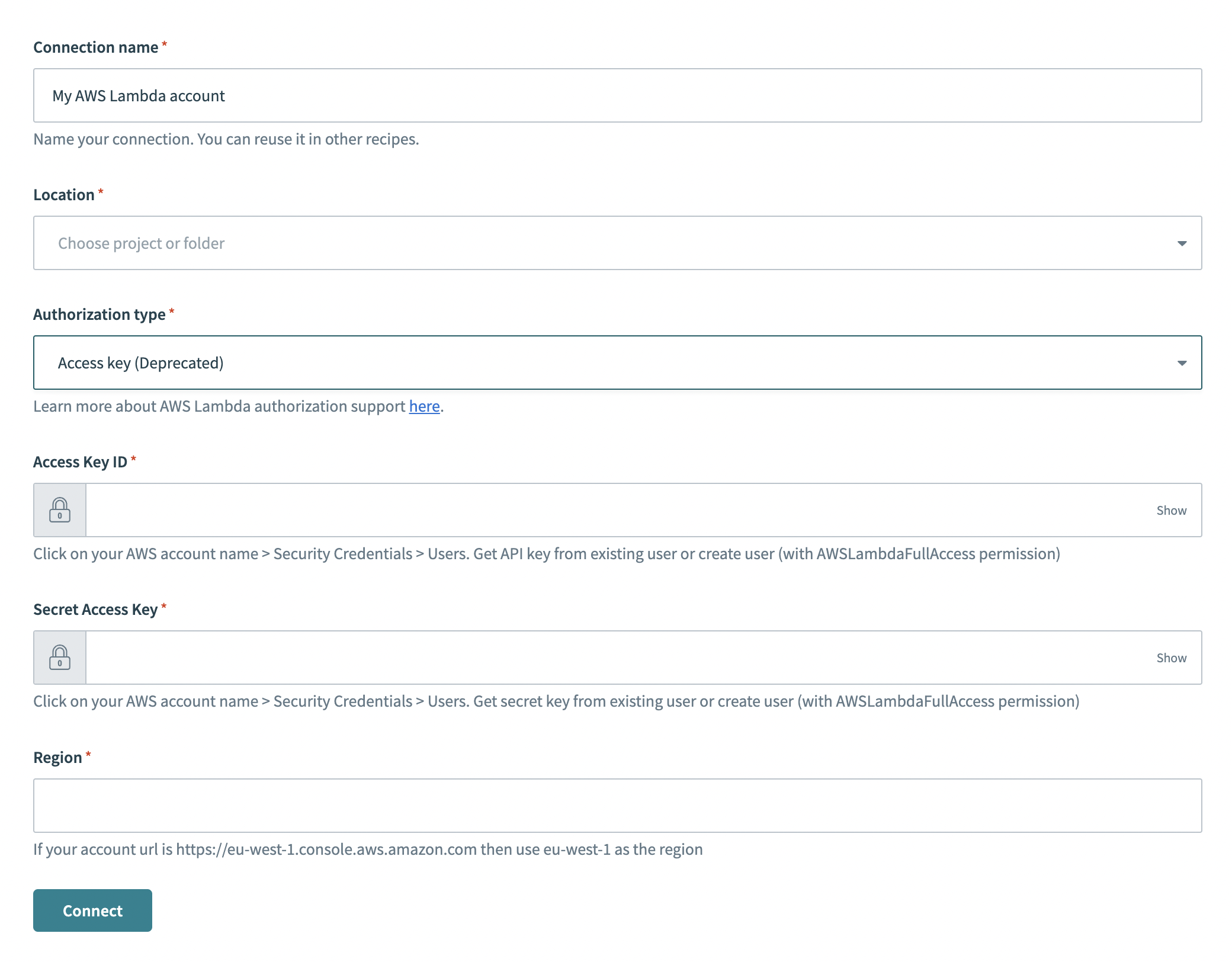 Authorization method - Access key
Authorization method - Access key
# IAM user policy requirements
Workato will perform operations in your AWS Lambda account as this IAM user. To use the full set of triggers and actions, the IAM user must have lambda:ListFunctions permission.
Refer to Create an IAM permissions policy for instructions on how to create your policy for Workato.
# Connect to AWS Lambda using IAM role
You can provision a Workato IAM role to connect to AWS Lambda. Provisioning a dedicated IAM profile allows the owner of the AWS Lambda instance to grant Workato access to AWS resources without sharing AWS security credentials. It also helps to maintain permission boundaries, including controlled access to specific AWS folders and actions that are permitted by the third-party application (for example, Workato).
Refer to the IAM role-based authentication for AWS page for instructions on how to create an IAM role for Workato and retrieve your Amazon resource name (ARN).
# Input fields for IAM role
- Fields for IAM role authentication.
- Connection name
- Give this connection a unique name that identifies which AWS Lambda instance it is connected to.
- Location
- The Workato project that requires the connection.
- Authorization type
- Select IAM role.
- IAM role ARN
- The IAM role ARN.
Note: Workato will generate a unique external id (for example,workato-user-84762). This value is different for every Workato user and must be provided when creating an IAM role in AWS Lambda. - Region
- Provide the region for this AWS Lambda account.
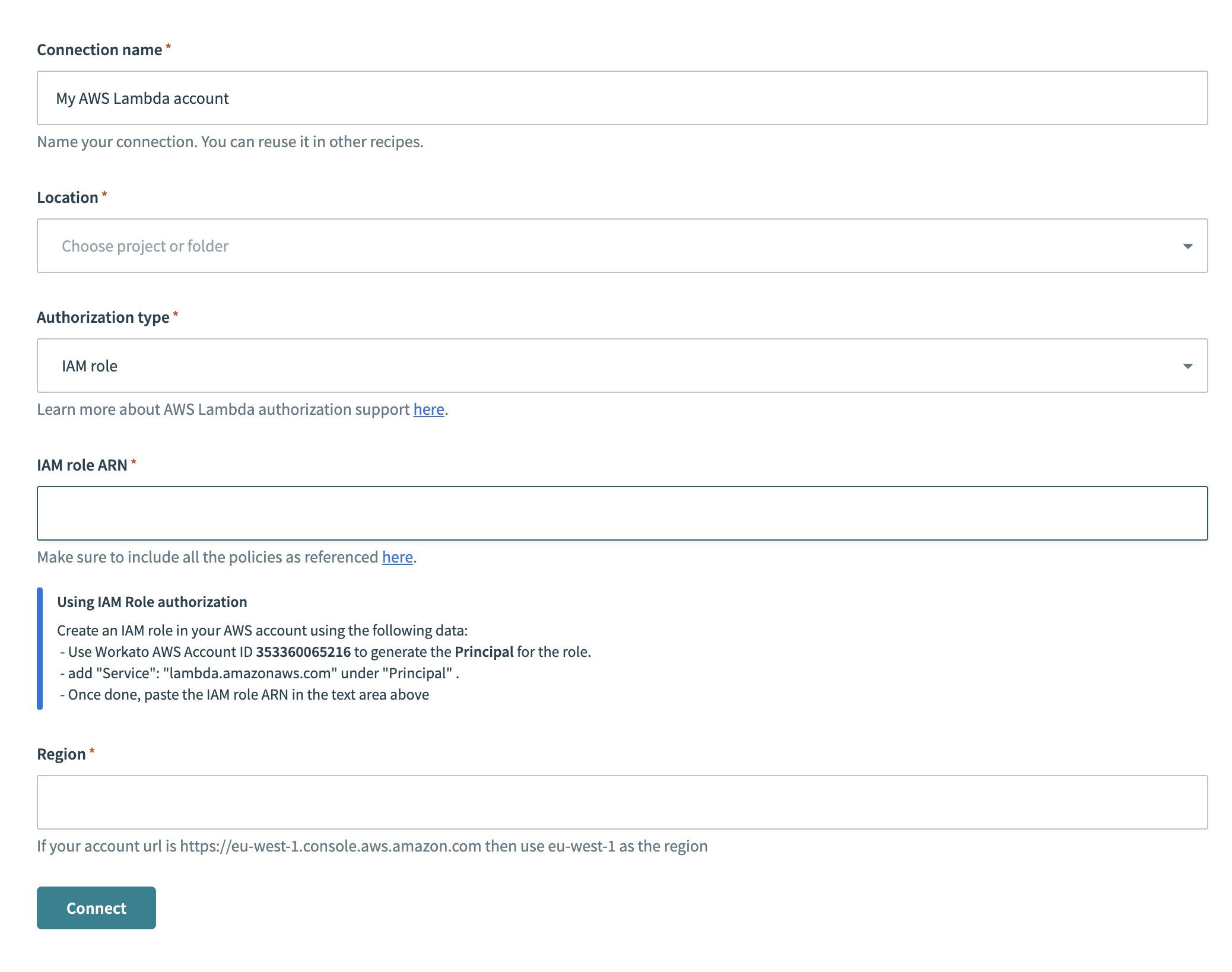 Authorization method - IAM role
Authorization method - IAM role
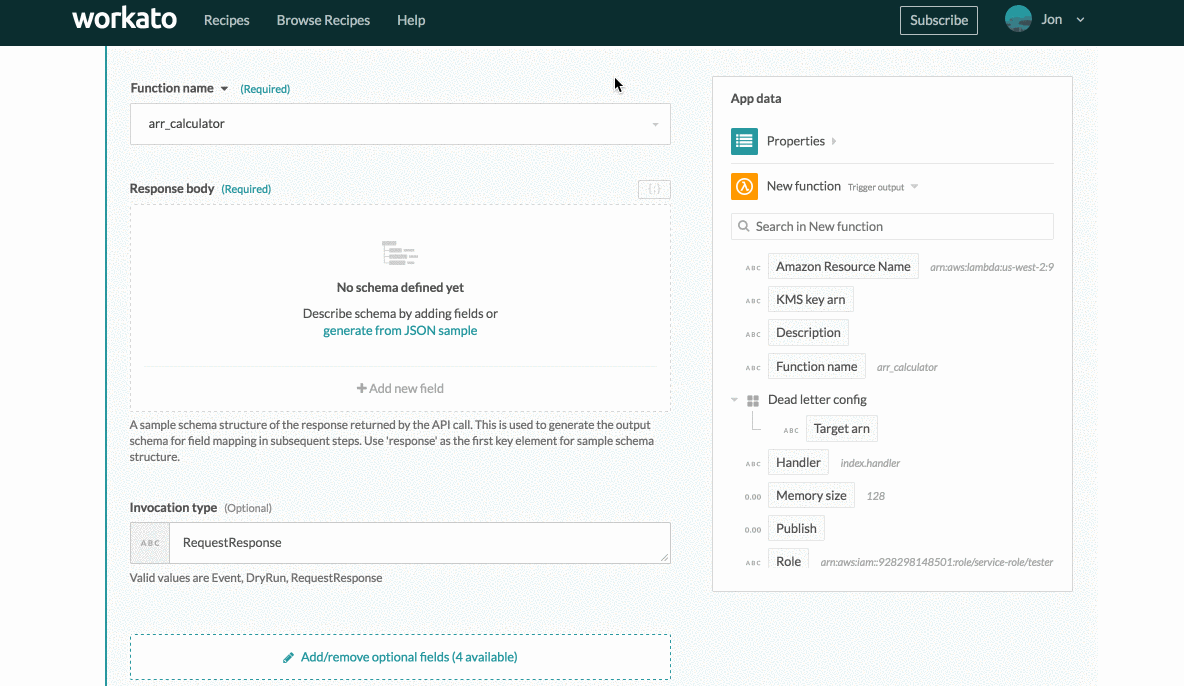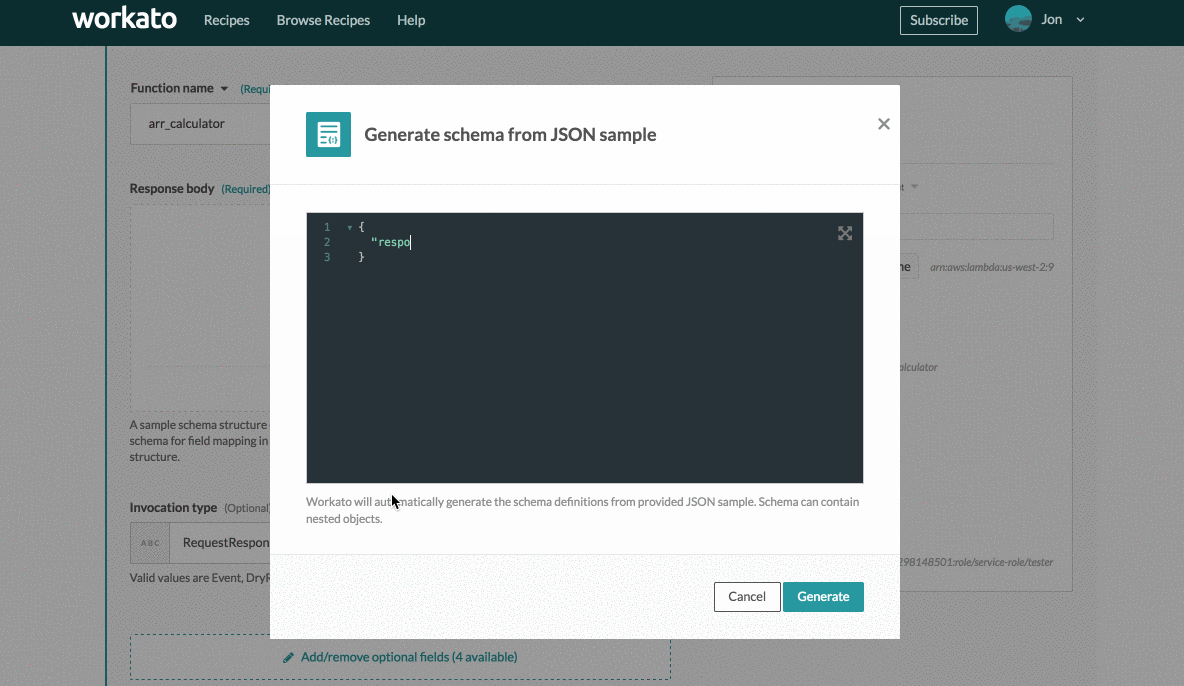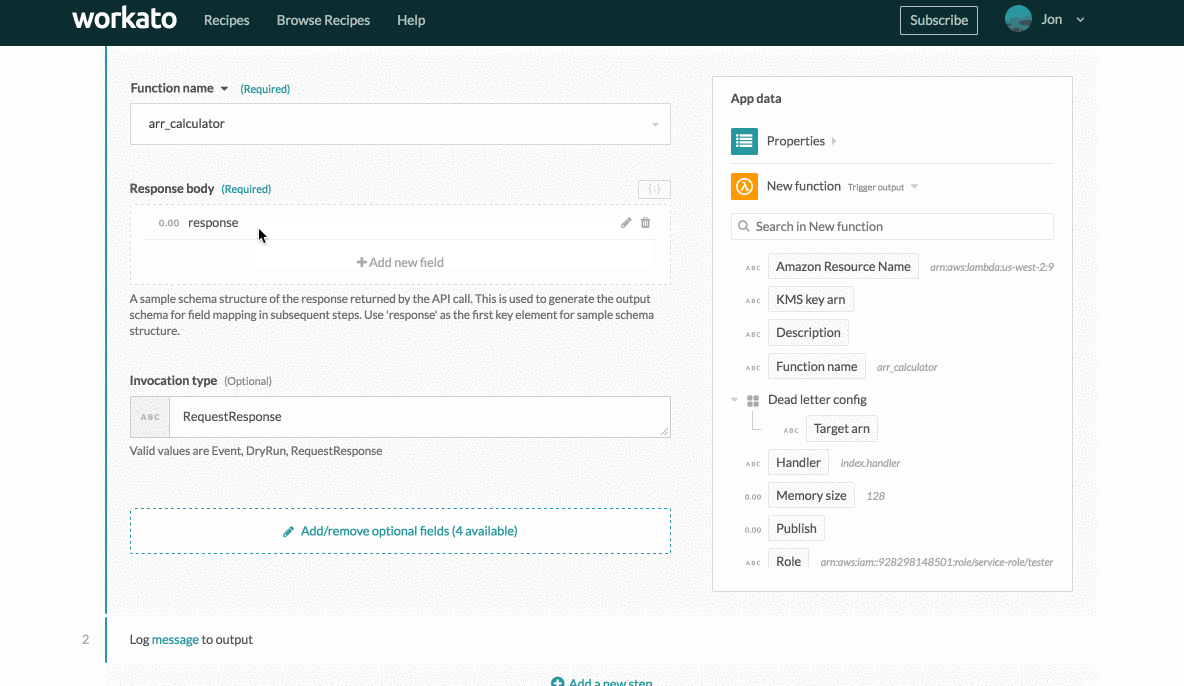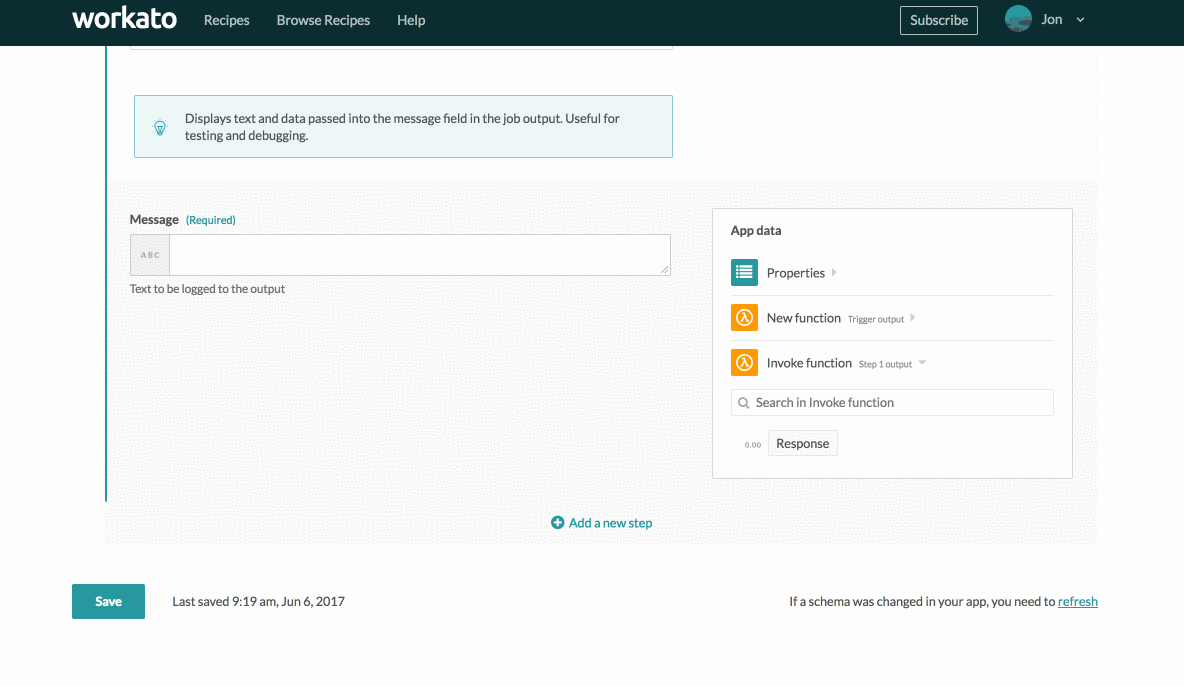
# Output schema definition
When working with Lambda functions as triggers or actions, you must define the output schema for each callable function. Each function's response is variable. This sample output schema is used to build the output datatree. This datatree allows you to use the data returned from the Lambda function in subsequent recipe actions.
To define the output schema, provide a sample response to the Response body input field. This should describe the data structure and schema of the output. There are 2 ways to configure this input field:
- Use a sample JSON
- Manually define schema using the schema designer widget
 Response body input field
Response body input field
The following example focuses on defining the output schema via sample JSON. Clicking generate from JSON sample displays the following schema designer widget.
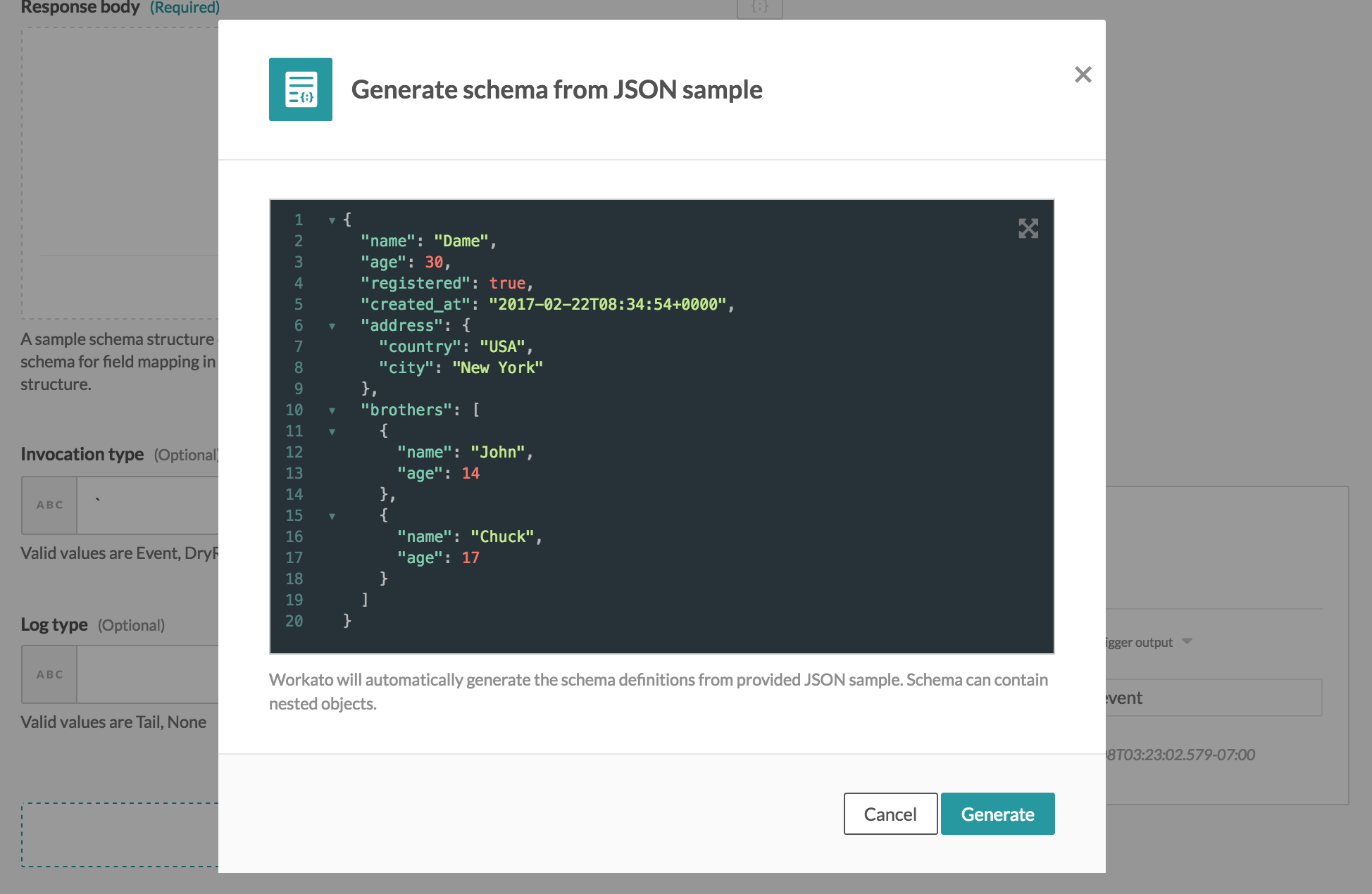 Schema designer widget
Schema designer widget
There are two typical formats for JSON:
- JSON response body
- Single primitive data
# JSON response
Workato requires all data be presented as key and value pairs. This is done so that we can map a value using its respective key. JSON data format is a good example. For the AWS Lambda connector, we require all response JSON to be wrapped in a parent response object. The response will look similar to the following example:
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Ee Shan",
"email": "eeshan@workato.com"
}
Wrap it in a parent "response" object:
{
"response": {
"id": 123,
"name": "Ee Shan",
"email": "eeshan@workato.com"
}
}
Insert the output JSON and click Generate. This generates the following output datatree:
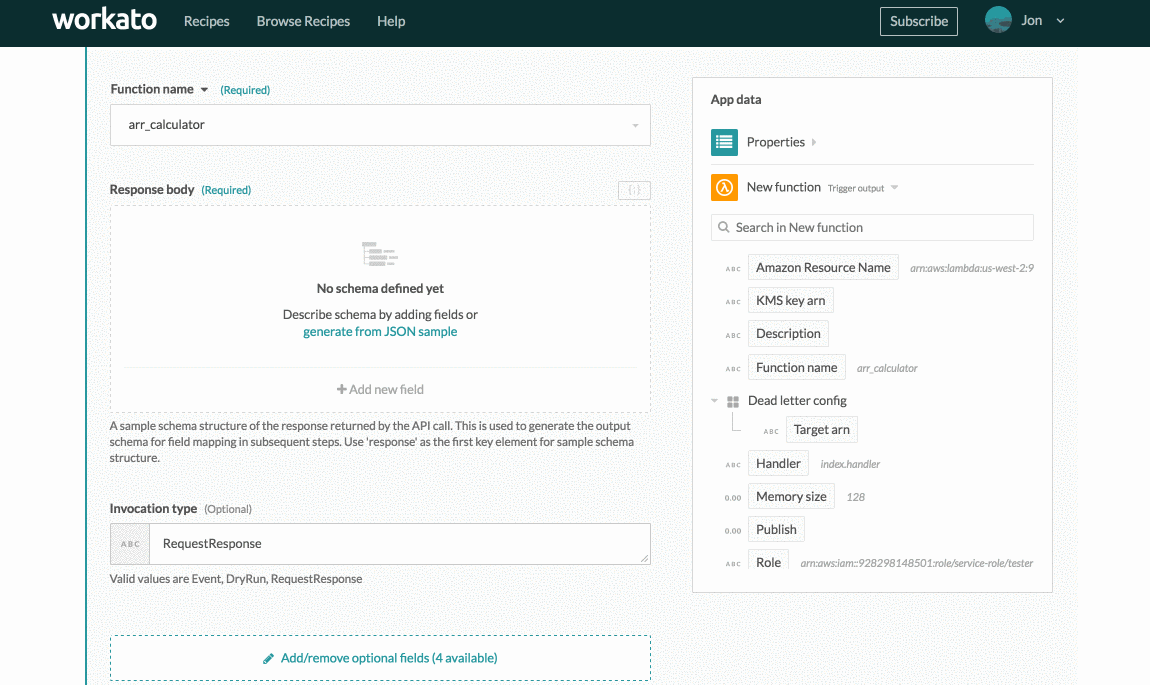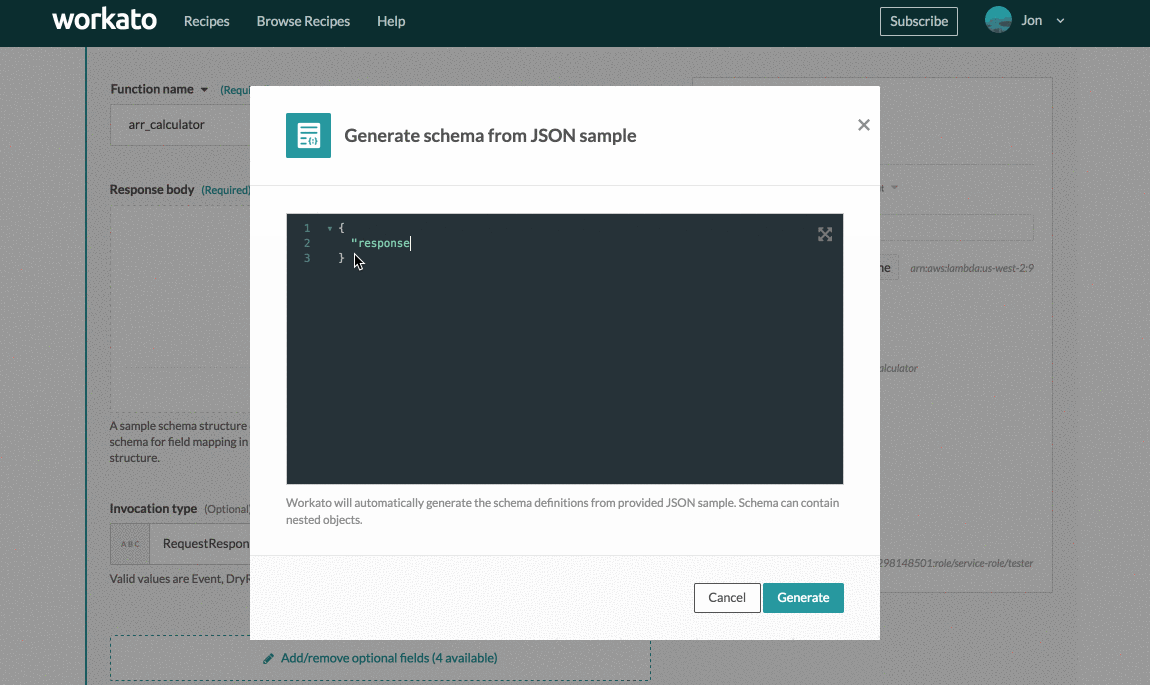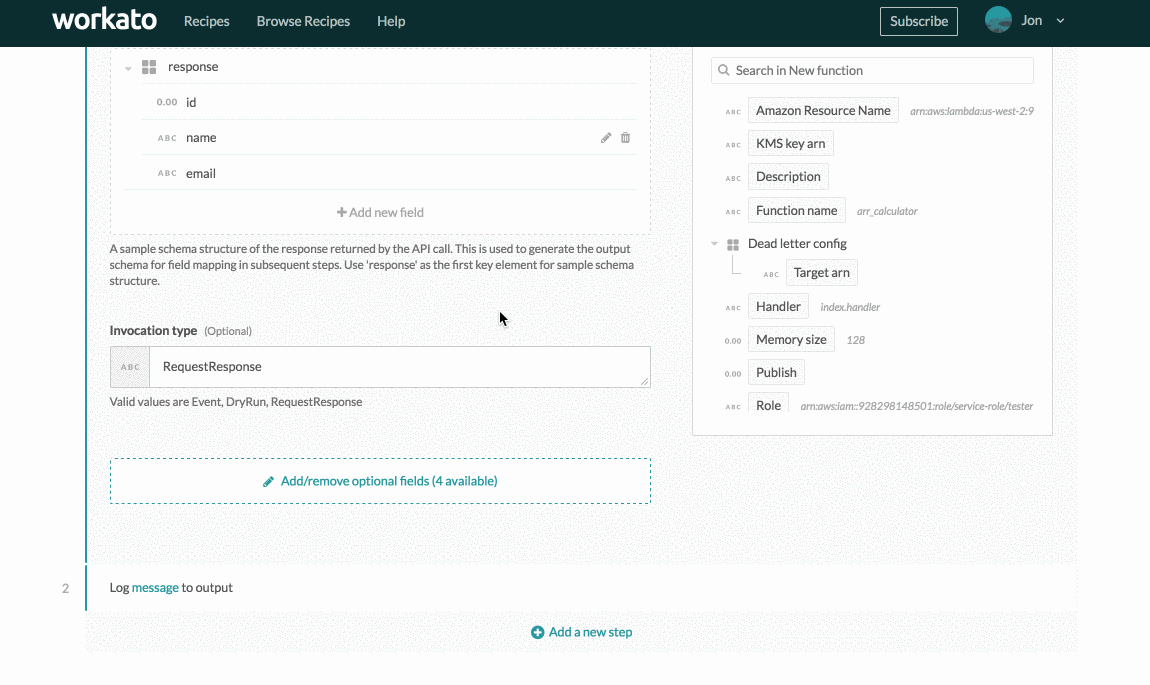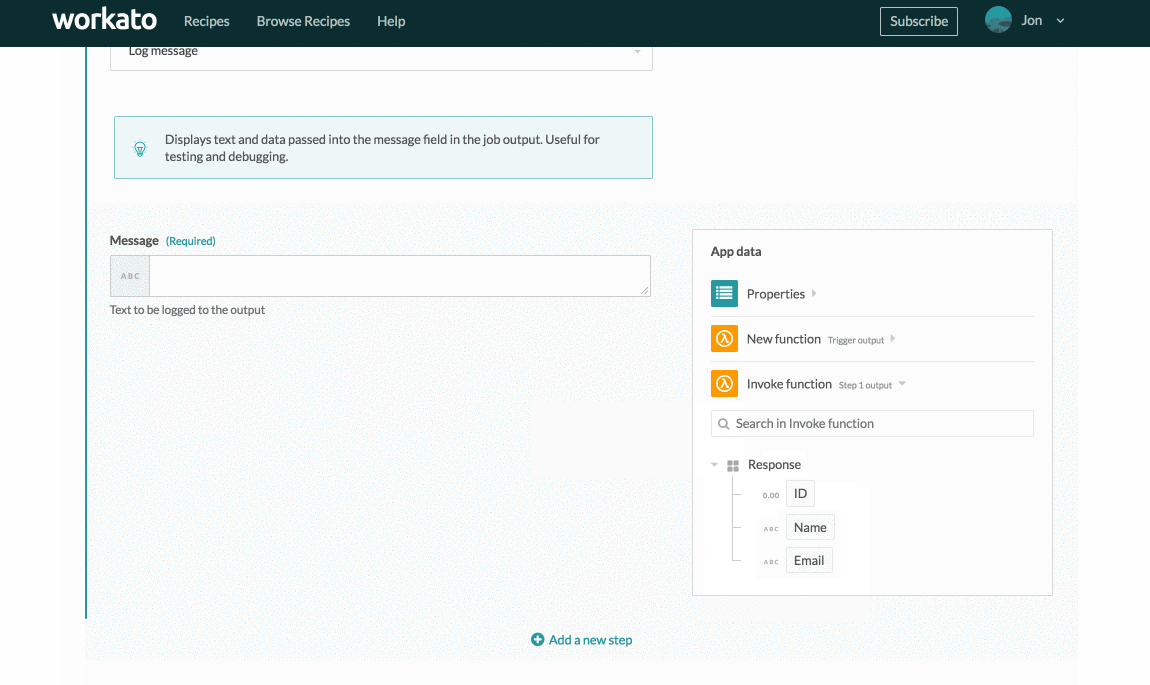 JSON body output datatree
JSON body output datatree
# Primitive data response
If the Lambda function returns non-JSON data structure, like a single string, integer, or a simple boolean value, it must be wrapped in a parent "response" object. The following example function returns an integer value of ID. A sample response will be:
4990
Wrap it in a parent "response" object:
{
"response": 4990
}
Insert the output JSON and click Generate. This generates the following output datatree:
 Primitive response output datatree
Primitive response output datatree
Last updated: 10/16/2023, 8:59:49 PM