# Google BigQuery
Google BigQuery (opens new window) is a serverless, highly scalable, and cost-effective cloud data warehouse with an in-memory BI Engine and machine learning built-in.
The Google BigQuery connector allows you to automate actions on datasets in your Google BigQuery instance, such as inserting rows or performing queries on existing datasets. You can also trigger recipes from new rows in dataset events.
# API version
The Google BigQuery connector uses the Google BigQuery API v2 (opens new window).
# How to connect to Google BigQuery
The Google BigQuery connector supports the following authentication methods:
- OAuth 2.0
- Service Account
SERVICE ACCOUNT AUTHENTICATION
You can use a service account to authenticate without a personal user account. For consistent use, Workato recommends service account authentication.
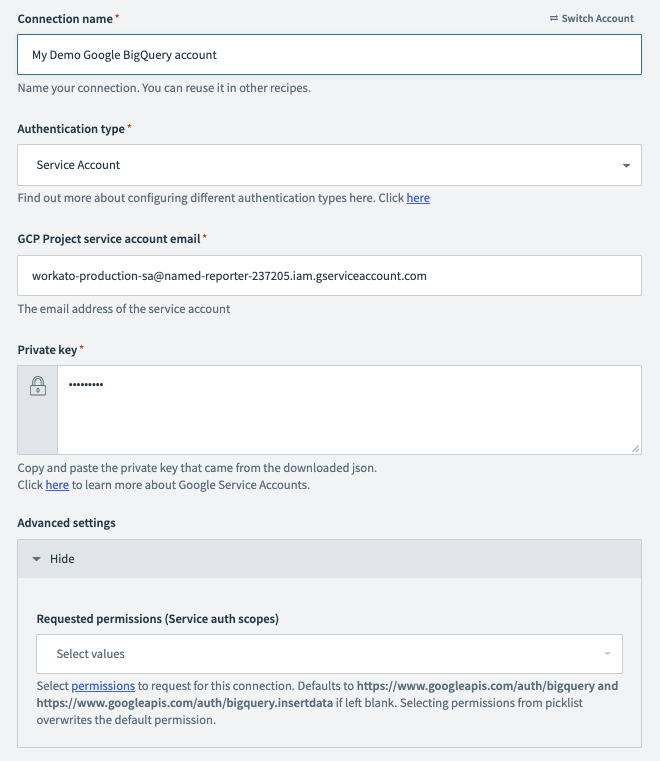
Complete the following steps to establish a connection to Google BigQuery in Workato:
Search for and select the Google BigQuery connector.
Enter a unique name for your connection in the Connection name field that identifies which Google BigQuery instance it is connected to.
Select the project or folder where you plan to store the connection from the Location drop-down menu.
Select OAuth 2.0 or Service account from the Authentication type drop-down menu. Choose OAuth 2.0 when using a user account to connect to Google BigQuery. Choose Service account when using a service account to connect to Google BigQuery.
Applicable to service account authentication. Enter the email address of your service account in the GCP Project service account email field.
Applicable to service account authentication. Enter the private key of your service account in the Private key field.
Applicable to service account authentication. Expand the Advanced settings section and select scopes to request your connection.
Click Sign in with Google.
Click Allow when prompted to authorize Workato to access your Google account.
# Service account authentication
A Google service account is a specialized Google account associated with a Google Cloud Project (GCP) that can run API requests on your behalf.
Service accounts provide the following benefits:
- Continuous operation: Service accounts ensure that operations continue even if individual user permissions change.
- Dedicated permissions: Service accounts can only access projects that you share with them.
- Dedicated API quotas: You can manage a service account's API quotas through GCP and request quota increases directly from Google.
Refer to the Google service account documentation (opens new window) to learn more about service accounts.
# Set up a Google service account
Complete the following steps to set up a Google service account:
Create a service account (opens new window) in your GCP project.
Go to IAM & Admin > Service accounts. Ensure your dashboard is scoped to the project that contains your service account.
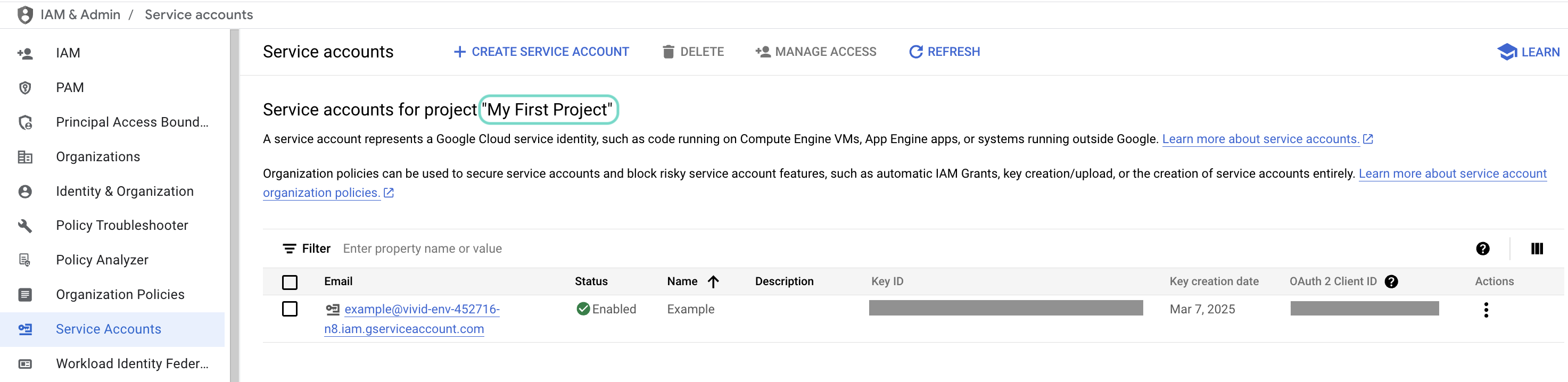 Check the scope of your dashboard.
Check the scope of your dashboard.
Click the Email of the service account you intend to use.
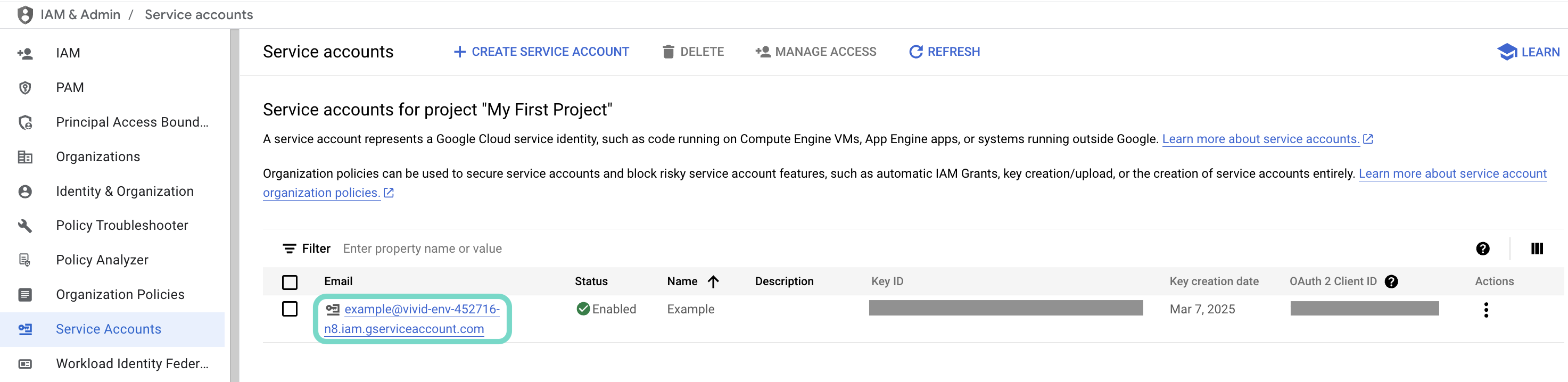 Click the Email of the service account you intend to use.
Click the Email of the service account you intend to use.
Copy the service account's Email and save it to configure your connection later.
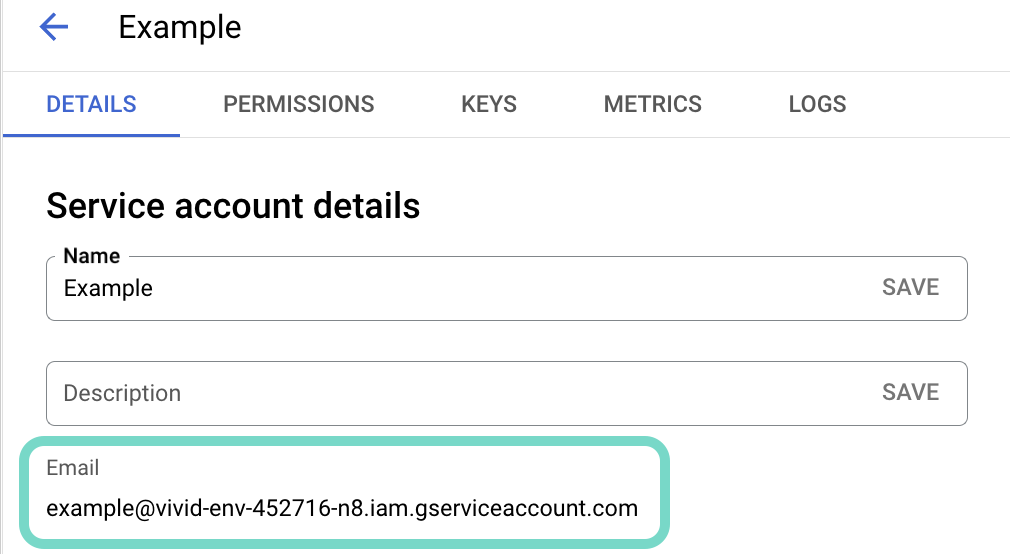 Copy the account's Email.
Copy the account's Email.
Go to the KEYS tab.
Generate a private key (opens new window) and download it in JSON format. You can only download the key once.
Open the JSON file, then copy the entire private key from -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- to -----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n (inclusive) and save it to configure your connection later.
Enable the Google BigQuery API, then return to Workato to finish setting up your connection.
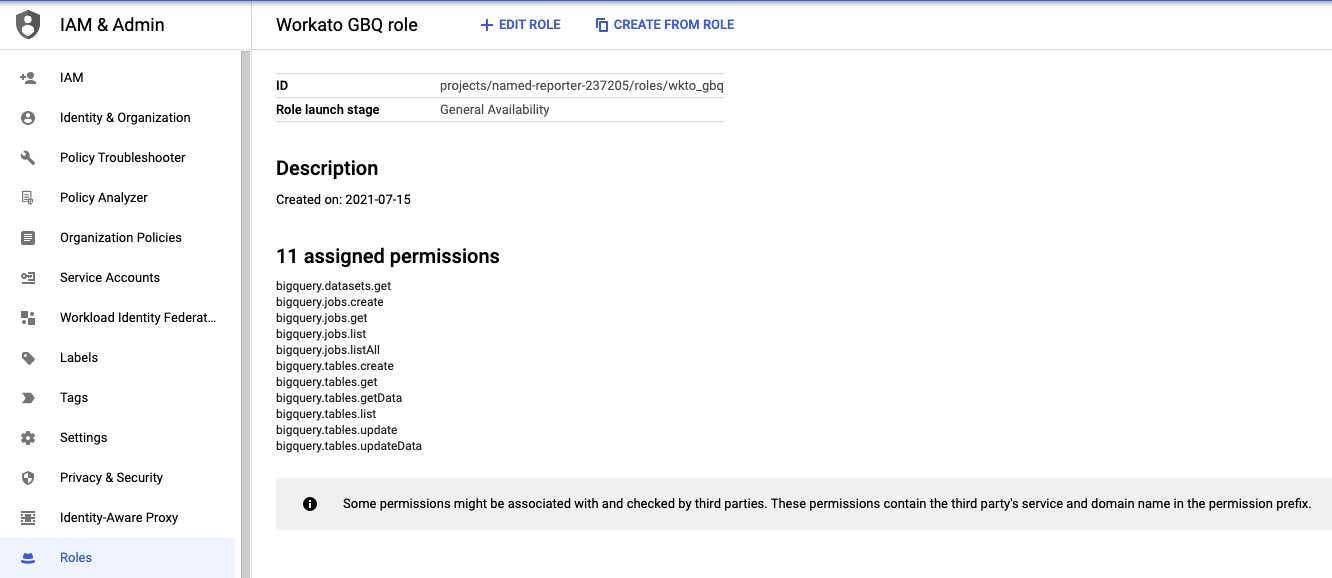
# Service account permissions
To use all triggers and actions in the Google BigQuery connector, you must give your service account the BigQuery Admin IAM role or a custom role with the following permissions:
- bigquery.datasets.get
- bigquery.jobs.create
- bigquery.jobs.get
- bigquery.jobs.list
- bigquery.jobs.listAll
- bigquery.tables.create
- bigquery.tables.get
- bigquery.tables.getData
- bigquery.tables.list
- bigquery.tables.update
- bigquery.tables.updateData
TIP
If you would like to only insert data with this connection on Workato, you may:
- Use the
BigQuery Data Editorrole. - Add the bigquery.jobs.create permission.
If you would like to only select data with this connection on Workato, you may:
- Use the
BigQuery Data Viewerrole. - Add the bigquery.jobs.create permission.
Refer to Google's documentation on creating custom roles (opens new window) and Google BigQuery permissions (opens new window) for more information.
SERVICE ACCOUNTS AND CUSTOM ROLES
If you're using a custom role for your service account, the project ID must be supplied directly in Workato. Otherwise, the Select project drop-down menu in Setup won't load, and you'll need to provide the project ID manually.
# Rate limits on Google BigQuery
Google BigQuery's rate limits (opens new window) on tables indicate that bulk insert operations on tables can only be performed 1000 times a day. Use the Insert row and Insert rows actions to bypass these limits.
# Using the Google BigQuery connector
After establishing a connection with the Google BigQuery connector, most actions require additional parameter inputs.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Project | The project to bill for the query. |
| Dataset | The dataset from which the action or trigger pulls possible tables. |
| Table | The table inside the dataset. |
| Location | The geographical location where the job should be run. |
# Single row versus batch of rows
The Google BigQuery connector can read or write to your database either as a single row or in batches. When using batch read actions or triggers, you must provide the a batch size. The batch size can be any number between 1 and 50000, with a maximum batch size of 50000.
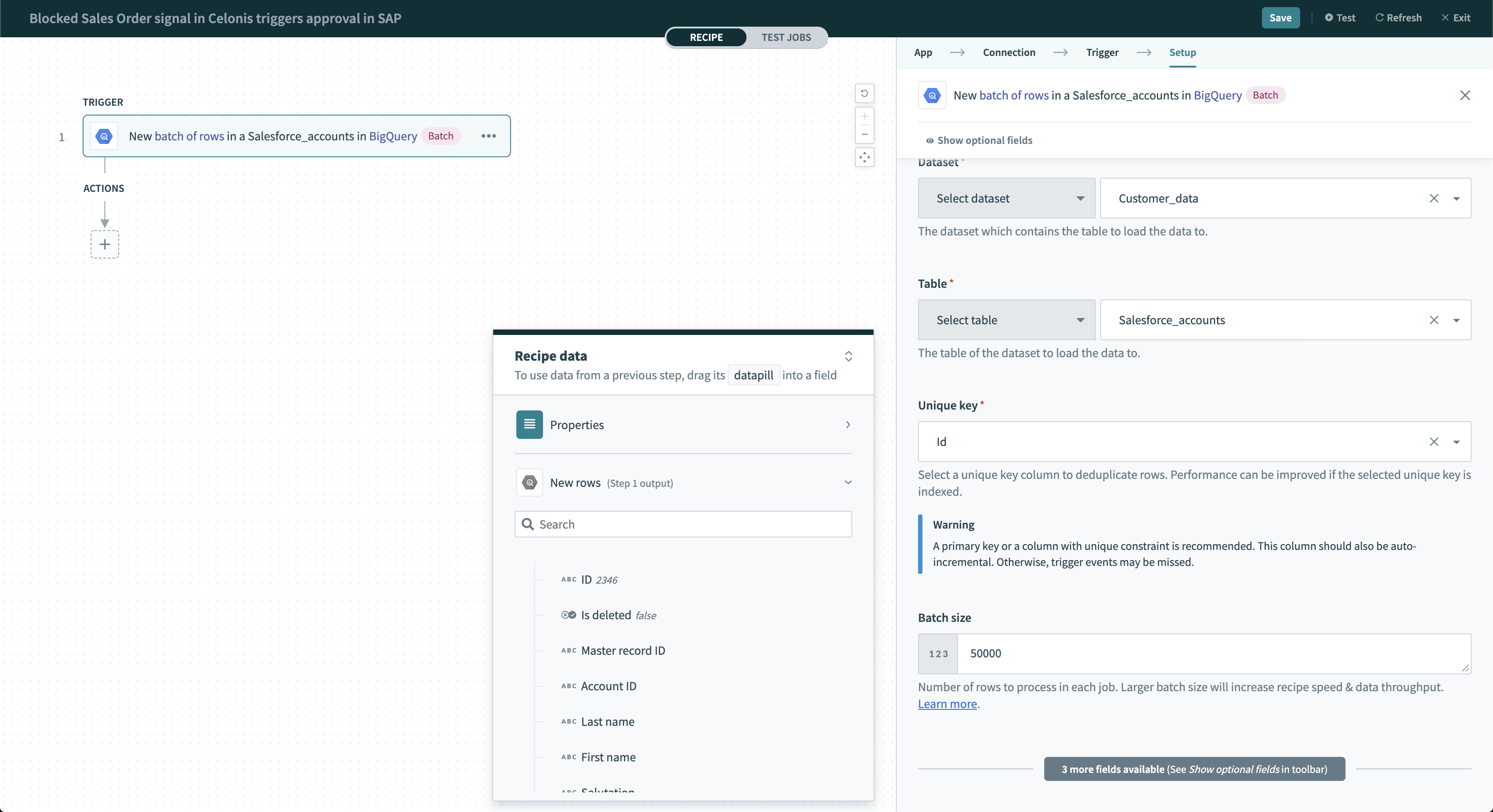 Batch trigger inputs
Batch trigger inputs
The output of single and batch triggers and actions also differ. For example, a single trigger that processes rows one at a time returns an output datatree that allows you to map data from that single row.
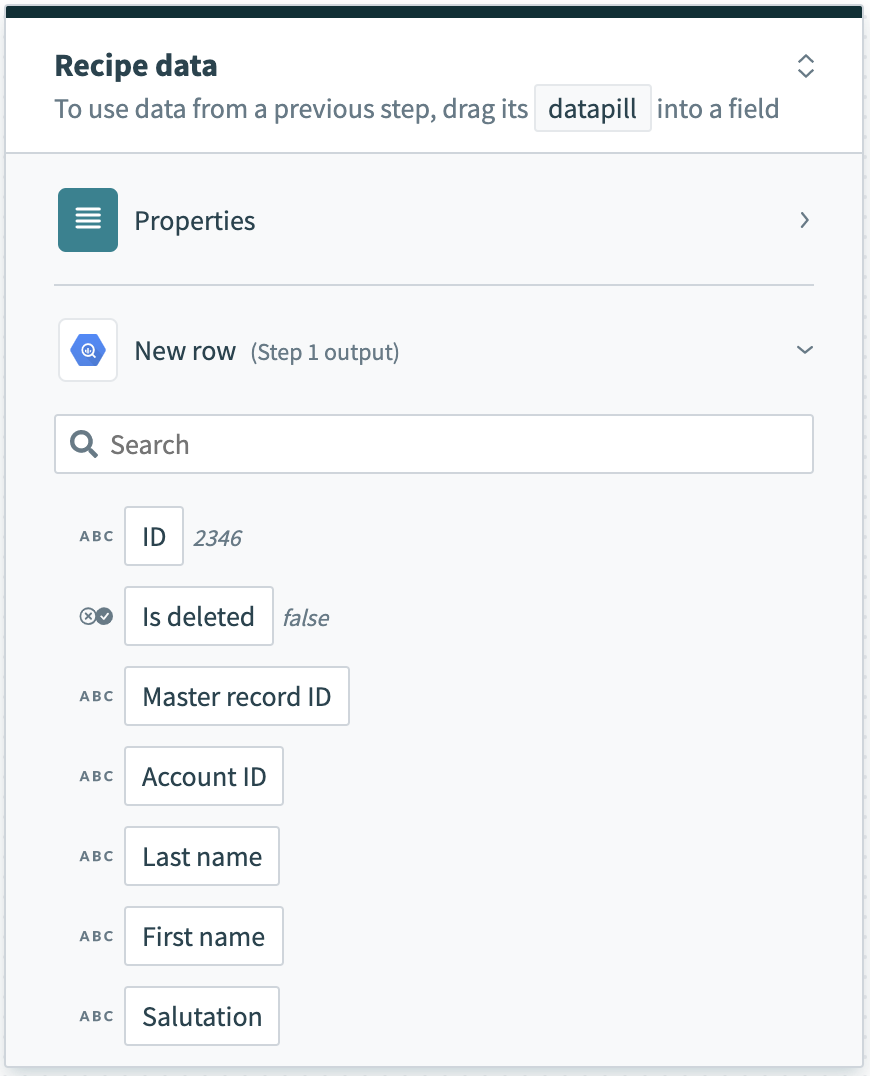 Single row output
Single row output
A batch trigger that processes rows in batches returns this data as an array of rows. The Rows datapill indicates that the output is a list containing data for each row in that batch.
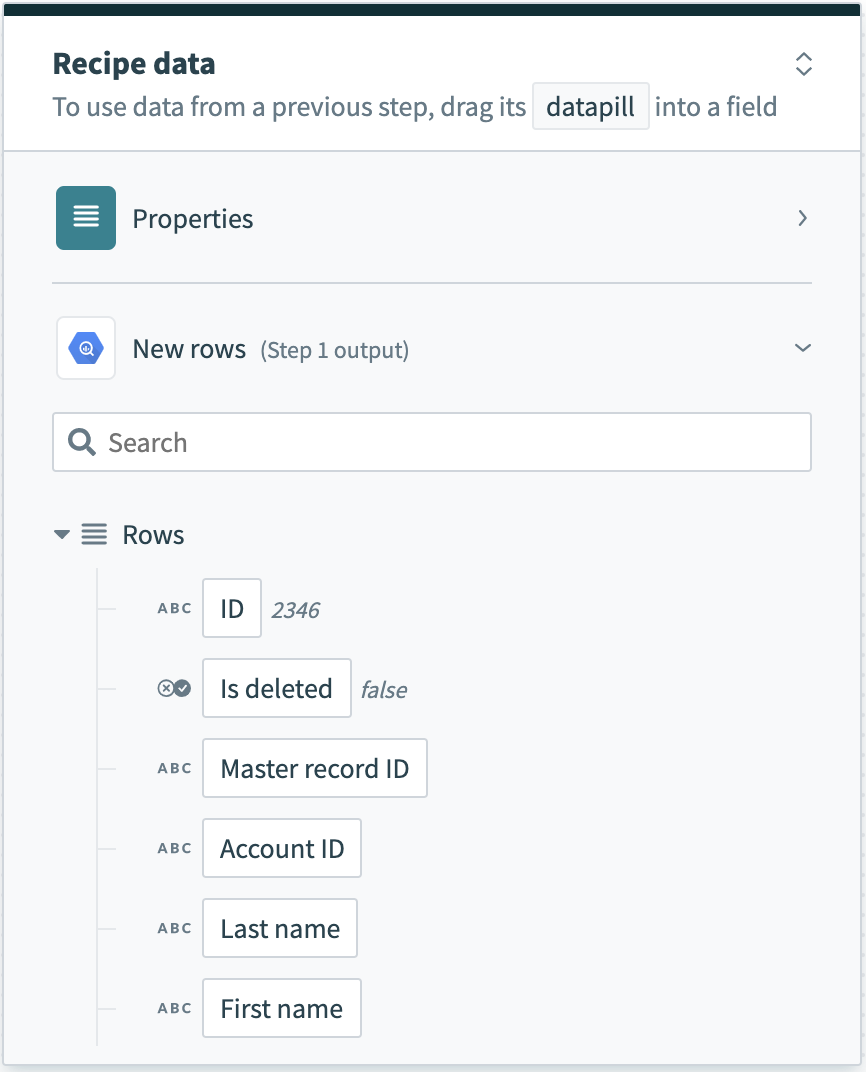 Batch trigger output
Batch trigger output
You must handle the output of batch triggers or actions differently. In cases where downstream batch actions accept Rows source list input fields, you can map the Rows datapill to process the entire array.
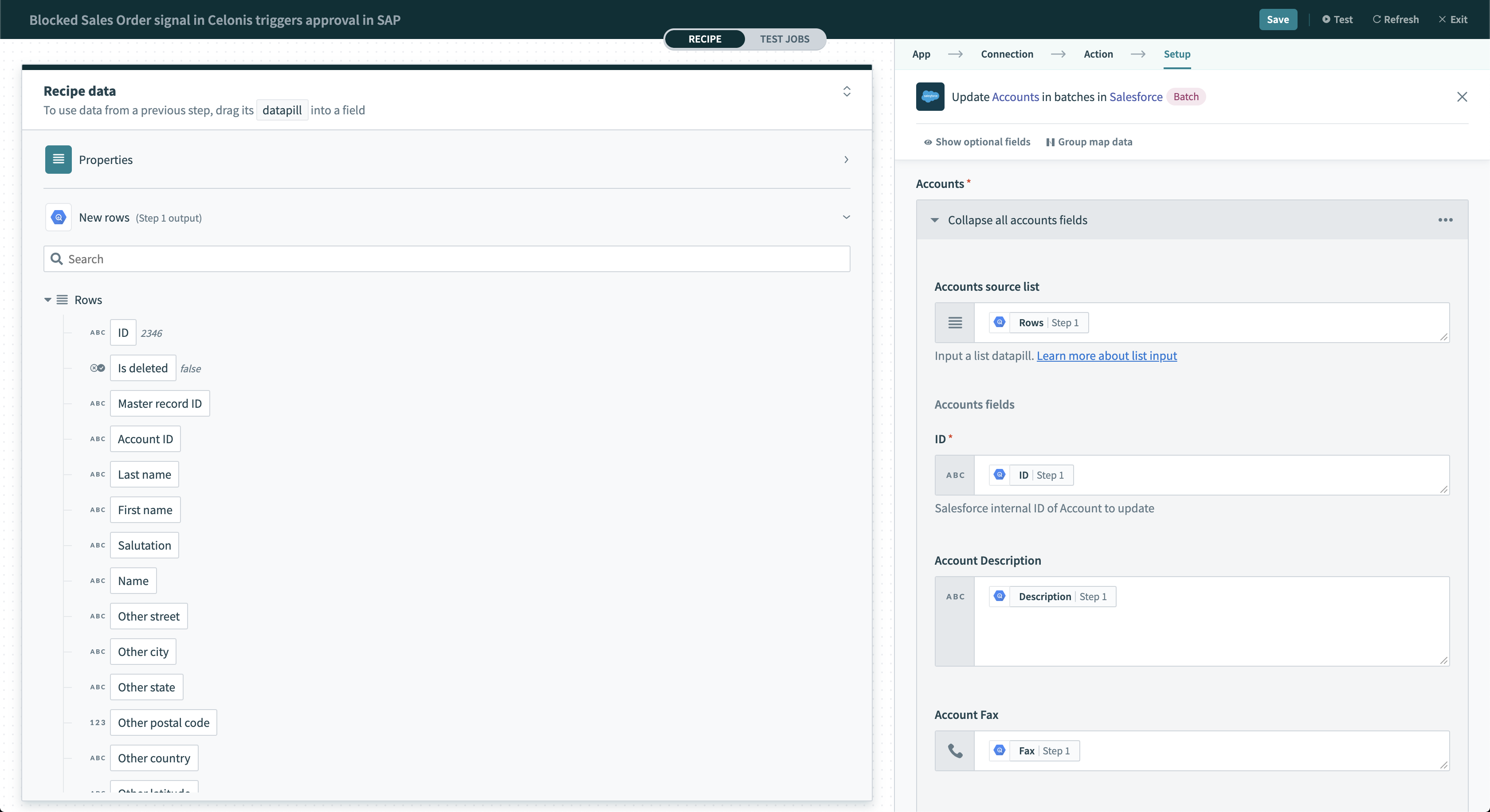 Using batch trigger output
Using batch trigger output
# WHERE condition
The WHERE condition input field allows you to filter and identify rows to act on. You can configure this field to:
- Filter rows to be picked up in triggers
- Filter rows in the Select rows action
- Filter rows to be deleted in the Delete rows action
Each request will use this clause as a WHERE statement. This should follow basic SQL syntax. Refer to the Google BigQuery documentation (opens new window) for a full list of rules for writing SQL statements compatible with Google BigQuery.
# Simple statements
Knowing the column's data types in Google BigQuery is important to build working queries. When comparing string values, you must enclose values in single quotes (''), and the columns used must exist in the table. When comparing integer values, the supplied value should not be enclosed in single quotes.
A simple WHERE condition to filter rows based on values in a single column looks like this:
string_column = 'USD' and integer_column = 1111
If used in a Select rows action, this WHERE condition will return all rows that have the value 'USD' in the currency column. Just remember to wrap datapills with single quotes in your inputs.
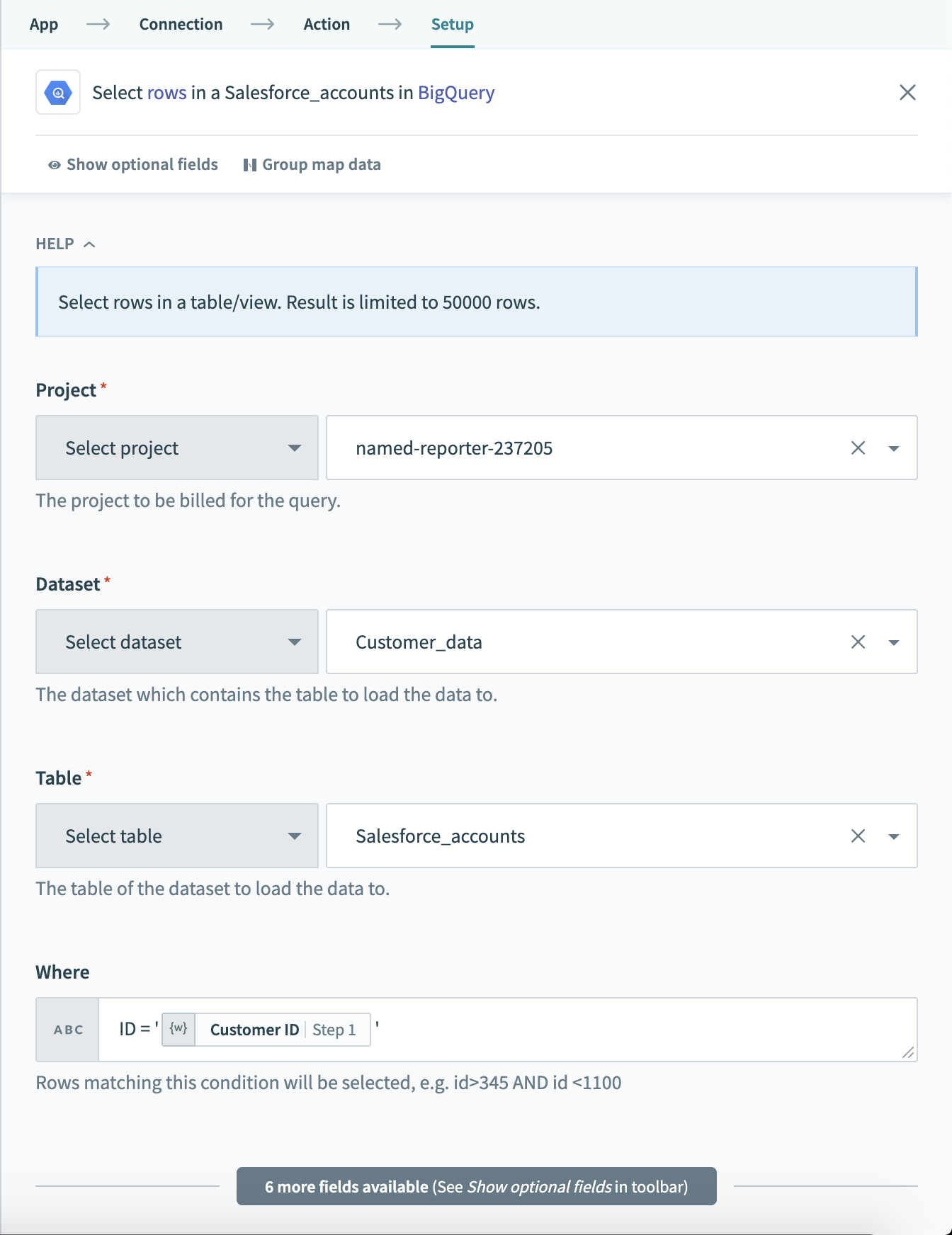 Using datapills in
Using datapills in WHERE condition
# Complex statements
Your WHERE condition can also contain subqueries. The following query can be used on the users table.
id in (select distinct(user_id) from zendesk.tickets where priority = 2)
When used in a Delete rows action, this query deletes all rows in the users table where at least one associated row in the tickets table has a value of 2 in the priority column.
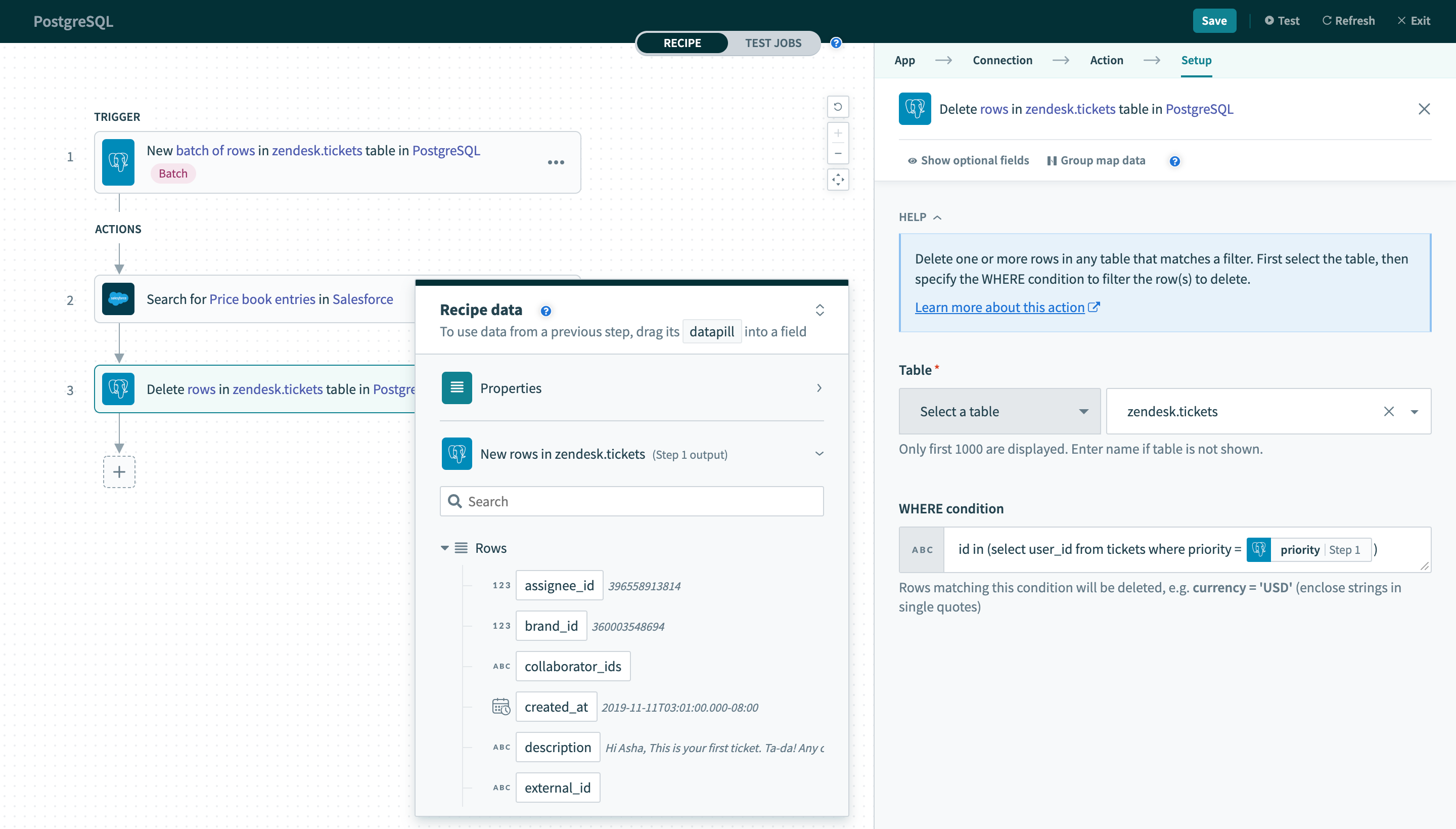 Using datapills in
Using datapills in WHERE condition with subquery
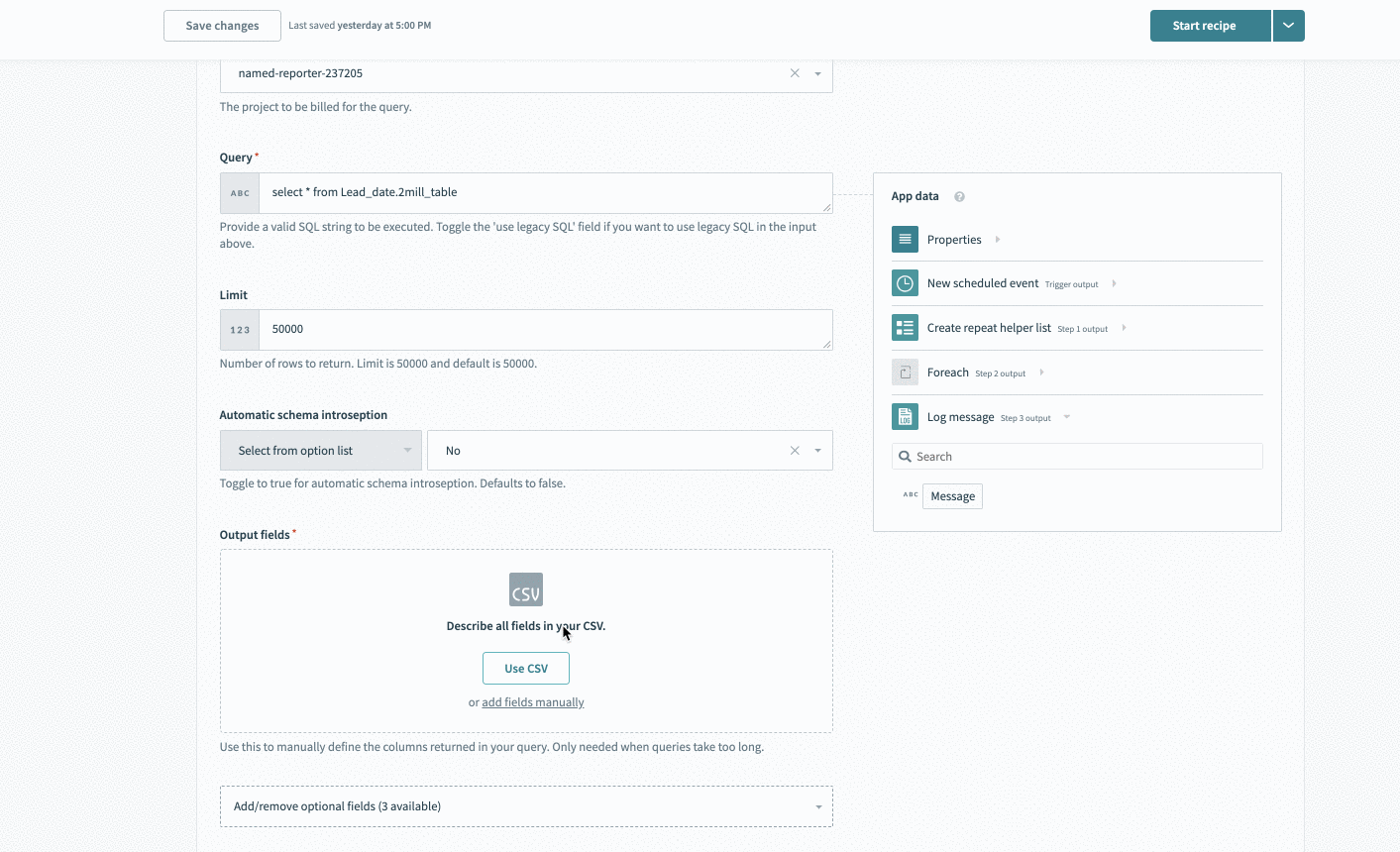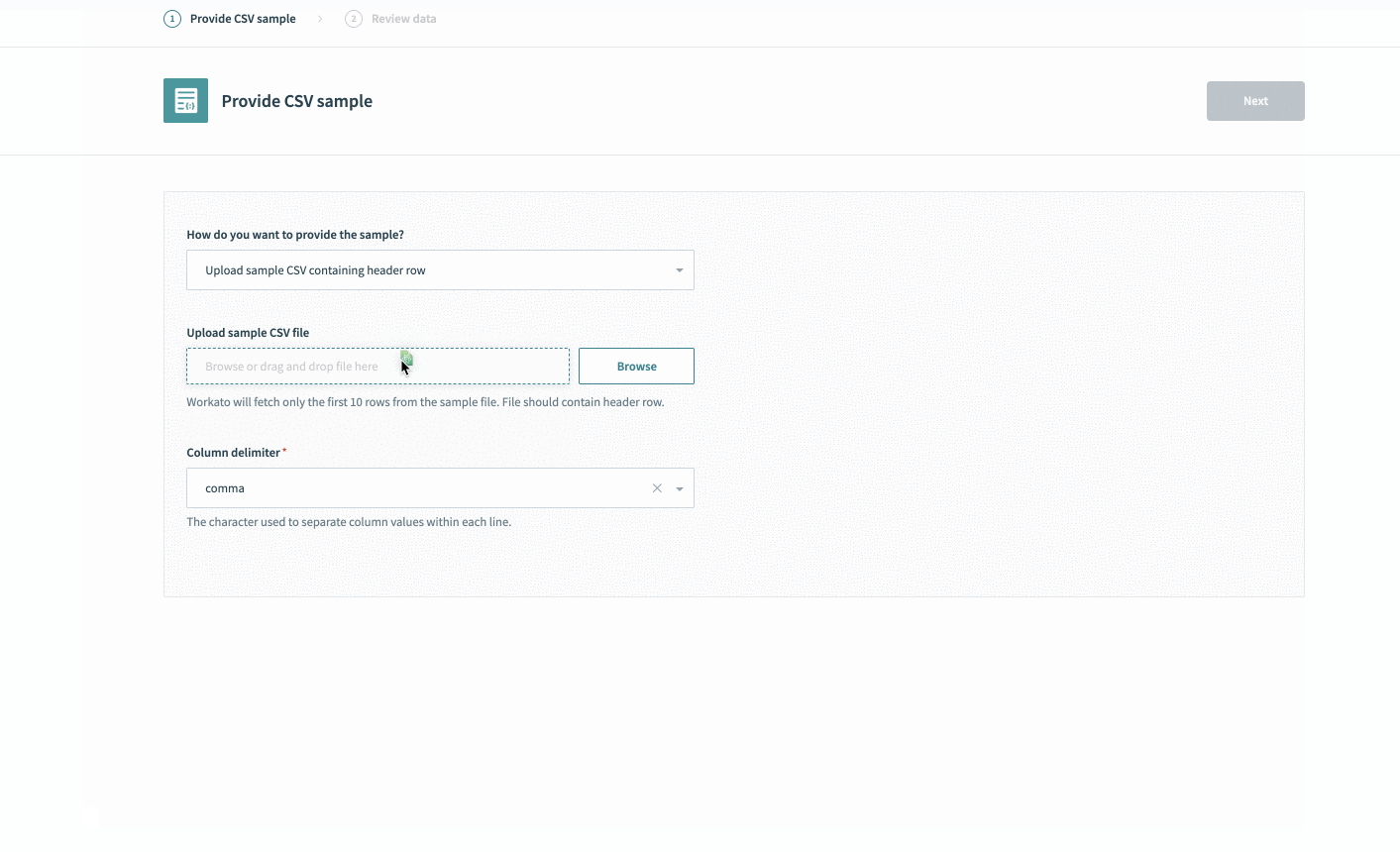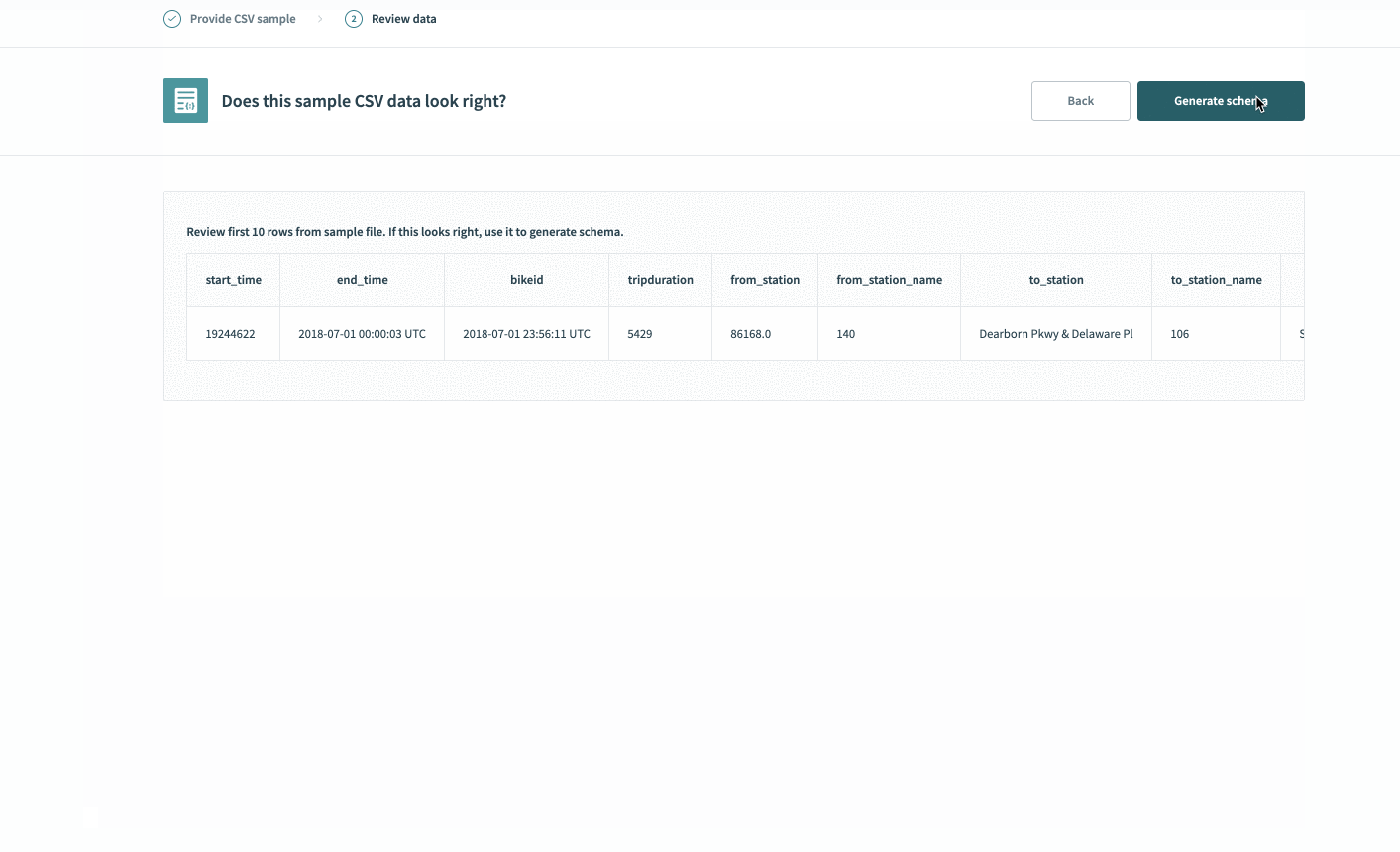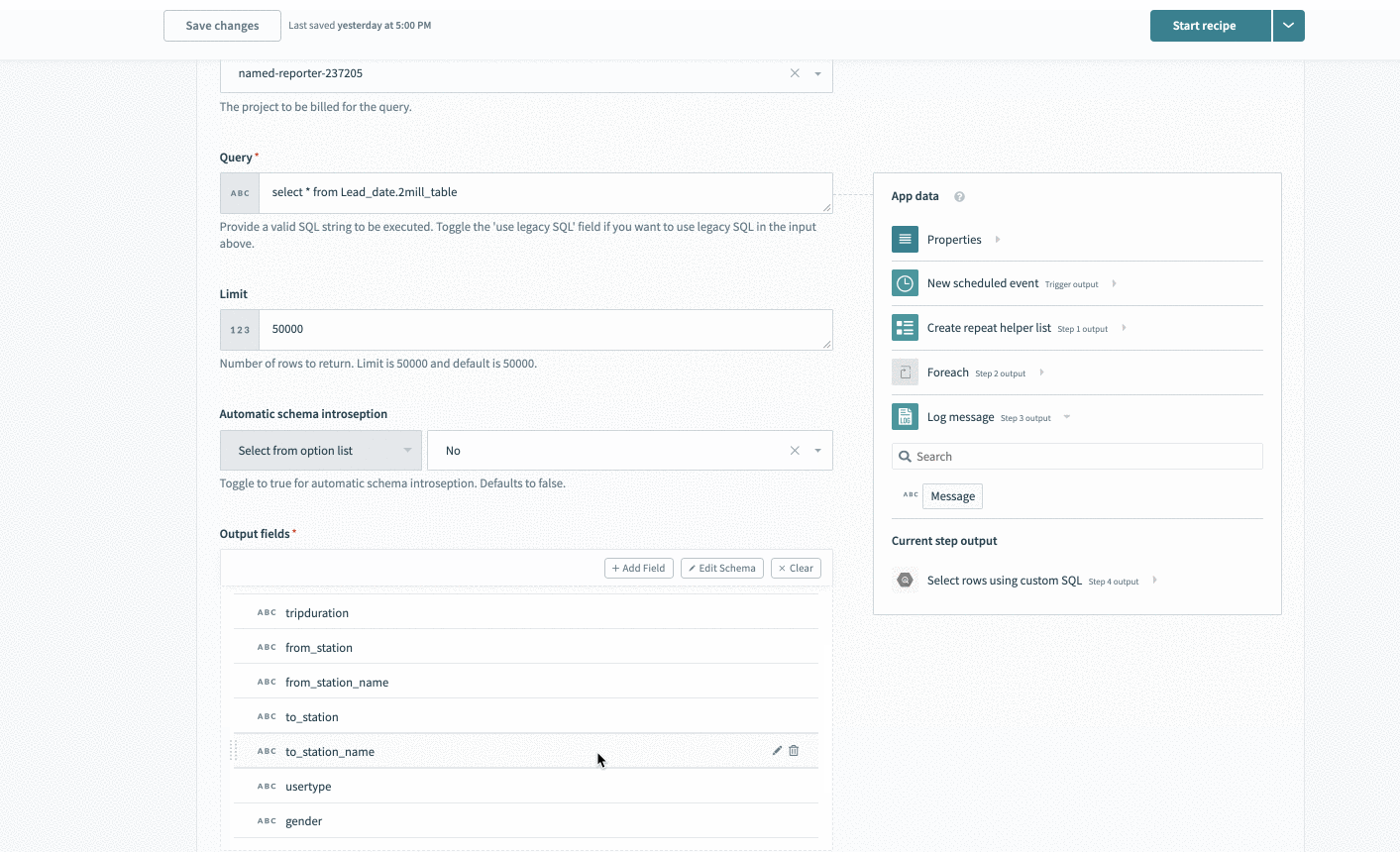
# Defining your output fields
Some Google BigQuery actions and triggers allow you to define the expected output columns of a query. This input field is available in the following triggers and actions:
- Scheduled query trigger
- Get query job output
- Select rows using custom SQL
Define your output fields in the output schema designer using our CSV uploader. In these cases, run a sample query in the Google BigQuery console and export a CSV.
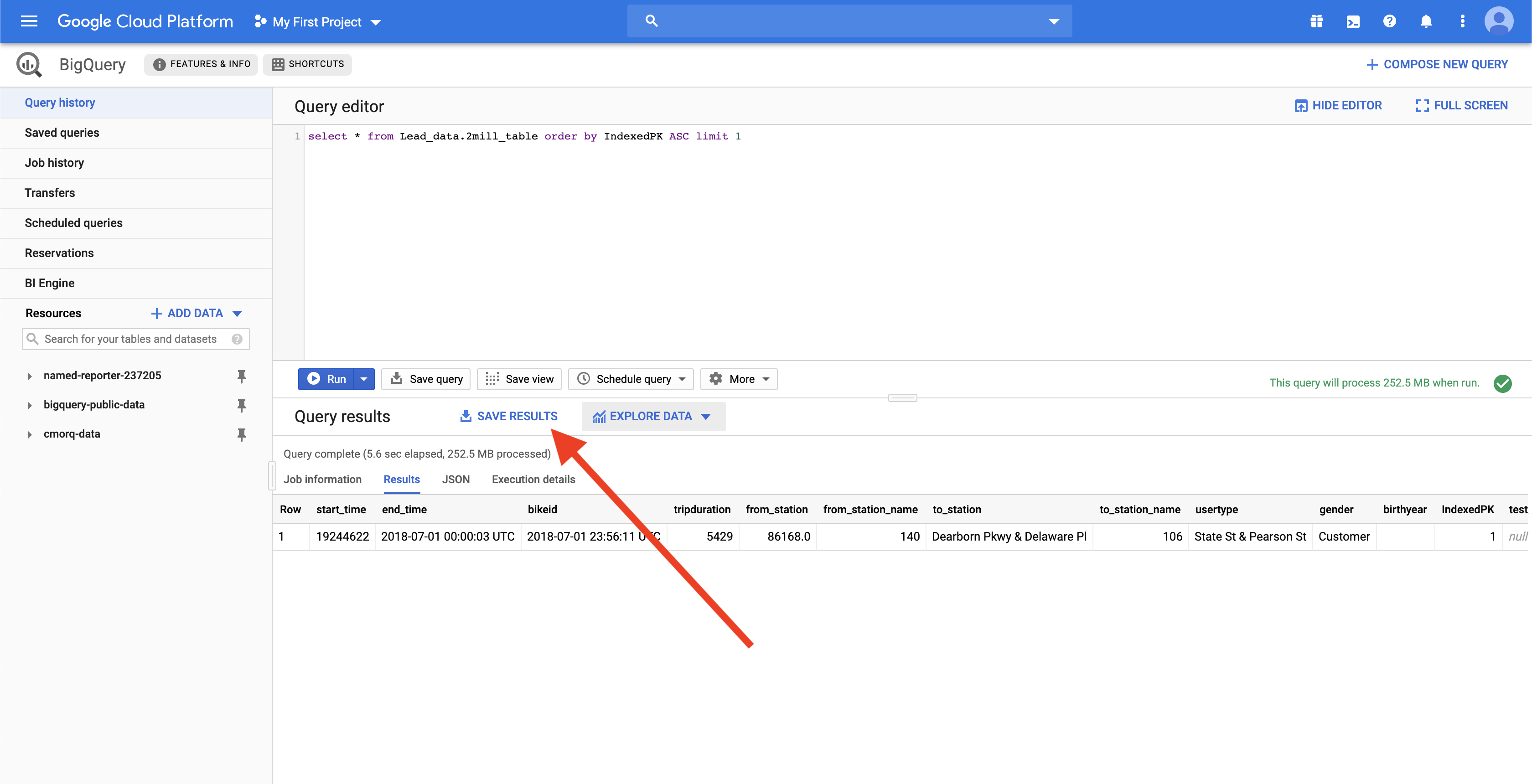
Upload this CSV into the schema wizard, and Workato automatically generates all fields.
Last updated: 1/8/2026, 8:06:18 PM