# NetSuite SOAP - Create standard and custom records in batch actions
The NetSuite actions Create standard records in batch and Create custom records in batch allow you to create multiple records in batches in NetSuite. These actions return the IDs of records successfully uploaded to NetSuite and the list of data that failed to upload to NetSuite.
These actions are synchronous, meaning that Workato sends a request to NetSuite to create a custom or standard record and then waits for Netsuite to complete before beginning other recipe actions. This is in contrast to our bulk actions which are asynchronous API calls - meaning Workato calls NetSuite and then must poll for the job status, which can cause delays and longer job times.
Synchronous actions can be especially useful during high volume data loads where ingestion time is critical.
API CONCURRENCY
Synchronous actions may result in more performance benefits in terms of ingestion but also consume your organization's API concurrency. By default, this is set to 5 but you may have purchased more from NetSuite. At API concurrency of 5, this means that you may have up to 5 concurrent NetSuite requests across your workspace but allows you to ingest up to 5 times more records than our asynchronous bulk actions. However, you should be conscious of your concurrency limits during large data volume loads, as this could also impact your other integrations that need concurrency. A simple way to limit API concurrency on Workato would be through Recipe Concurrency. Buying more API concurrency increases the number of batches you can process simultaneously in your workspace. Contact your Netsuite Customer Support Representative for more information.
One thing to note - Netsuite bulk actions, whilst less performant, utilize significantly less API concurrency since jobs are processed in a single queue on Netsuite.
# Limitations
Workato limits the processing time for each action to 180 seconds, but in some cases, NetSuite can take much longer to process synchronous API calls containing large batches of records. This can result in a timeout error in Workato. To prevent this, we recommend reducing your batch size for this specific record to ensure optimal processing in less than seconds.
# Input
Select the Standard record or Custom record that you plan to create.
In our example, we create a standard record and select Customer.
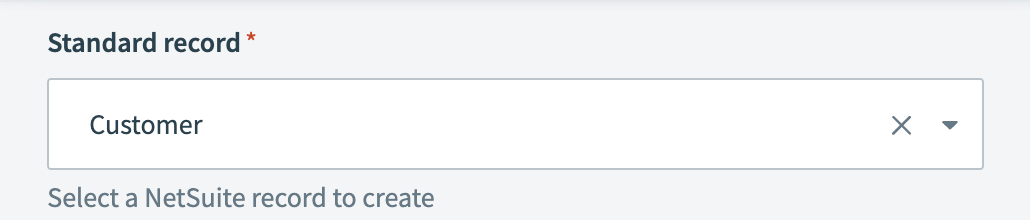 Select a NetSuite record
Select a NetSuite record
# Field configuration
Configure the following input fields to shortlist the NetSuite fields you plan to use. The action's input and output then display only these fields. This optimizes your NetSuite API requests and makes working with complex NetSuite objects containing hundreds of fields easier.
In this example, we used the fields Company name, External ID, and the custom field Product interest.
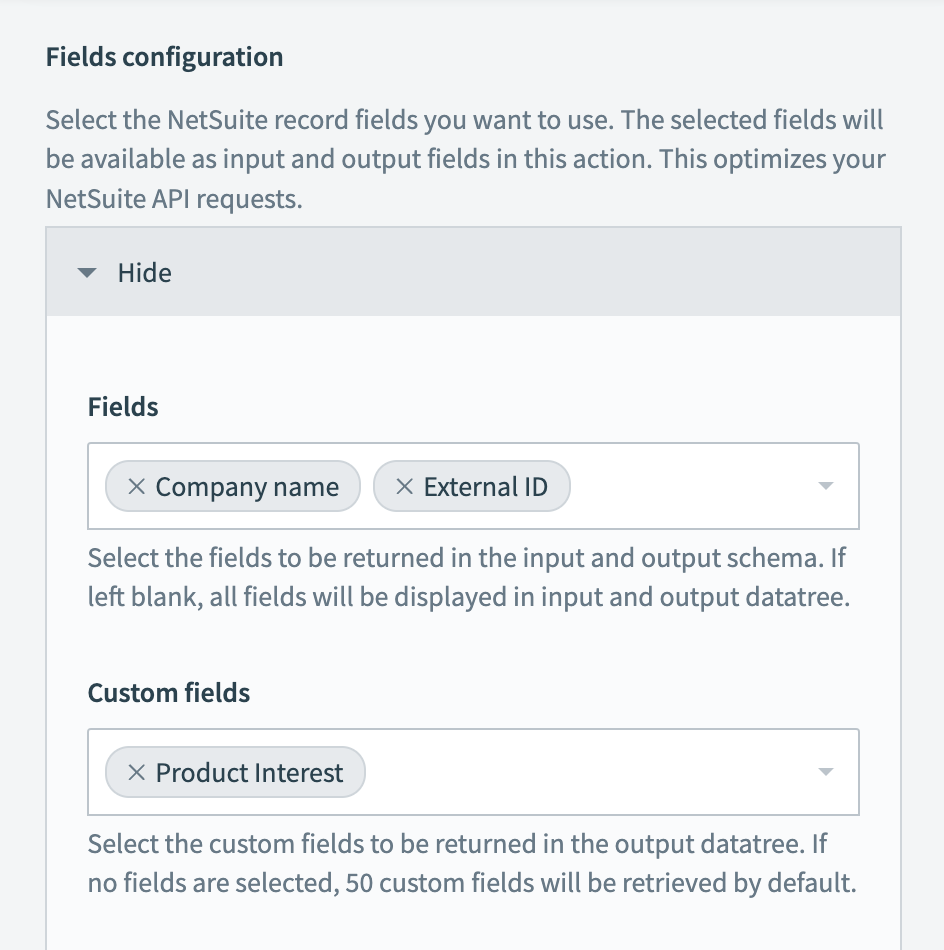 Shortlist NetSuite fields
Shortlist NetSuite fields
Fields
The Netsuite record's main fields that you plan to shortlist. If left blank, all fields are displayed in the input and output datatree.
Custom fields
The Netsuite record's custom fields that you plan to shortlist. If no fields are selected, Workato retrieves 50 custom fields by default.
Custom segment schema
If your Netsuite record has a custom schema, you can define the custom schema here.
Line item custom fields
The Netsuite record's line item custom fields to be shortlisted. If no fields are selected, Workato retrieves 50 custom fields by default.
Line item custom segment schema
If your Netsuite line item has custom schema, you can define the custom schema here.
# Record
The name of this section is dynamic and is based on the Standard record or Custom record you selected in the previous step. In our example, this section is named Customers. Here are the data mappings for creating NetSuite records.
In the following example, we map the data from the Box trigger New CSV file in directory to NetSuite record Customer. Notice that it only displays the shortlisted fields Company name, External ID, and Product interest.
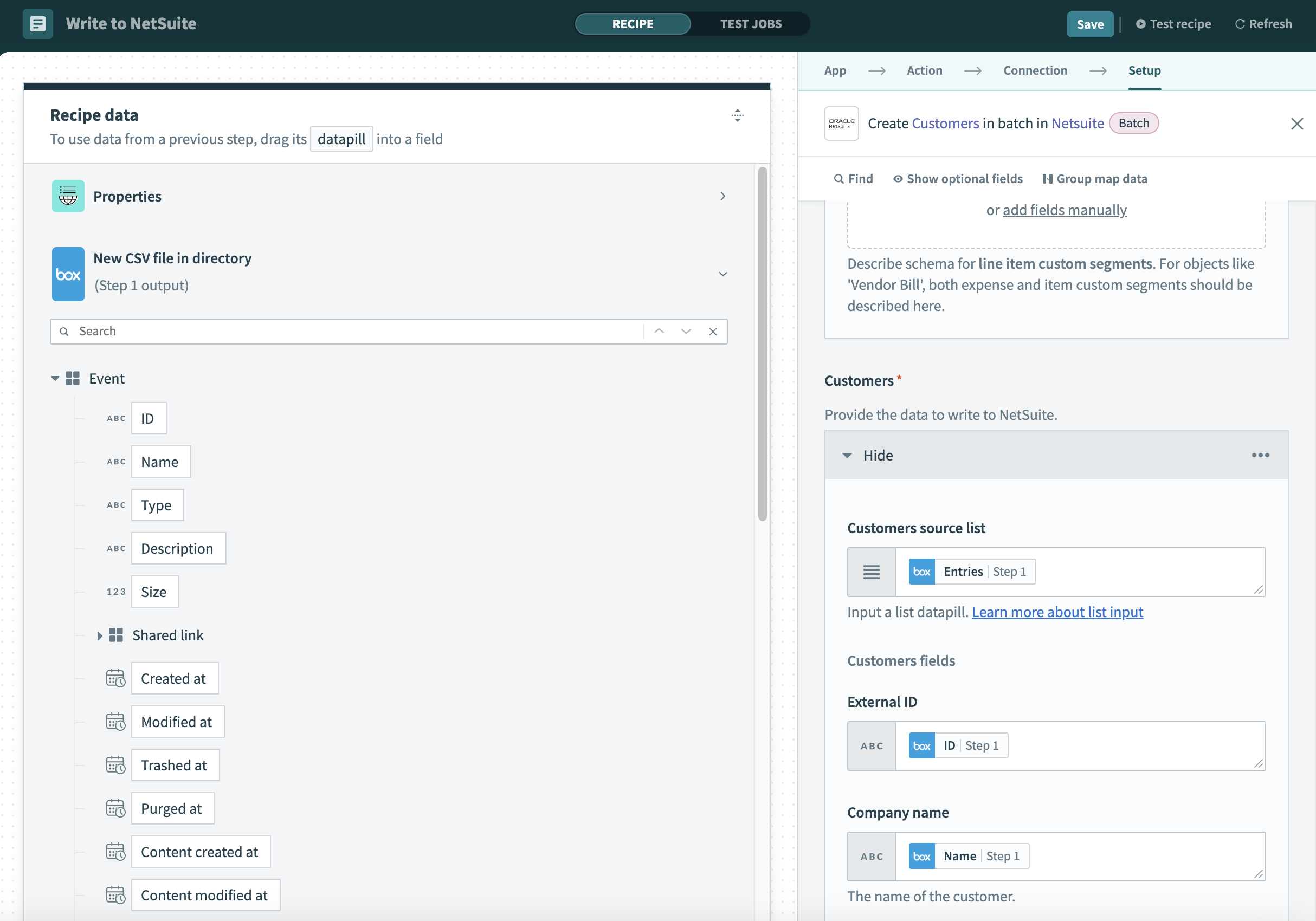
These are the input fields:
Record source list
Provide a list datapill.
For example, use a list of rows in a CSV file. The action automatically iterates through all items in the list, and maps them to NetSuite records.
Record fields
Map the datapills under the preceding list datapill.
For example, the CSV column names under the CSV Rows list datapill. This action automatically iterates through all items in the list, and maps them to NetSuite records.
# Output
Number of processed records
The total number of records processed.
Number of successful records
The number of records successfully created.
Number of failed records
The number of records failed to be created.
Successful records
A list datapill containing all successful records.
Use this to iterate through all records in the list.
The data fields of each record are:
Internal ID
The internal ID of this record.
External ID
The external ID of this record.
Record
Contains all data fields of this record.
List size
Number of successful records in this list.
Failed records
A list datapill containing all failed records.
Use this to iterate through all records in the list.
The data fields of each record are:
Error
A list datapill containing all errors of this record.
Use this to iterate through all errors in the list.
Record
Contains all data fields of this record.
List size
The number of failed records in this list.
Last updated: 1/16/2026, 4:23:47 PM