# Redshift - Select actions
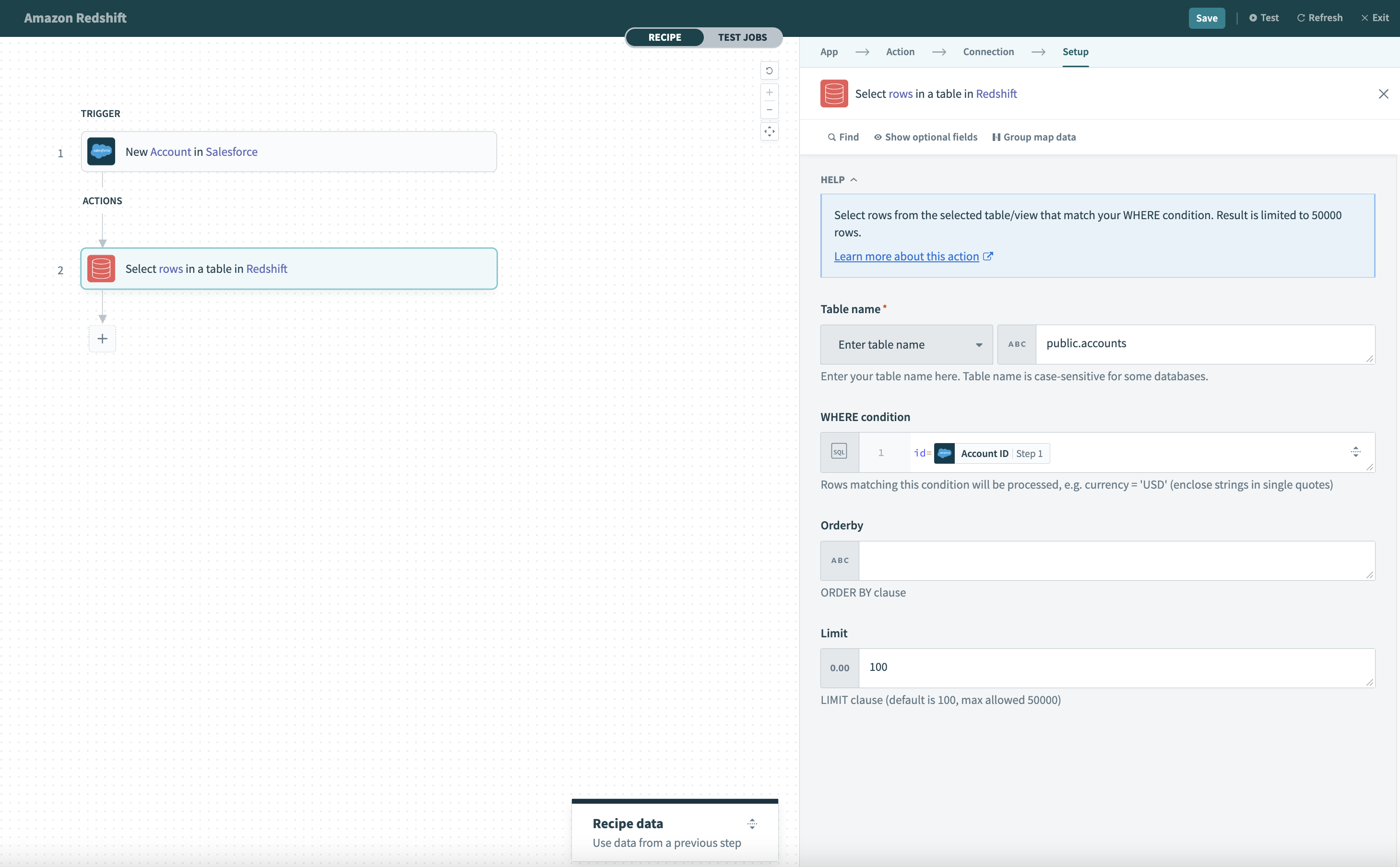
# Select rows
This action lets you select rows based on certain criteria defined by a WHERE condition. Rows from the selected table that match the WHERE condition will be returned as the output of this action.
 Select rows action
Select rows action
# Table
First, select a table to work with. This can be done either by selecting a table from the pick list, or toggling the input to text mode and typing the full table name.
# WHERE condition
Next, provide a WHERE condition to filter rows. This condition can be as simple as filtering a single record by it's ID.
id = 123
Alternatively, it can be used to select multiple rows based on values in one or more columns.
status = 'closed' and priority = 1
Complex WHERE conditions with subqueries can also be used. Refer to the WHERE condition guide for more information.
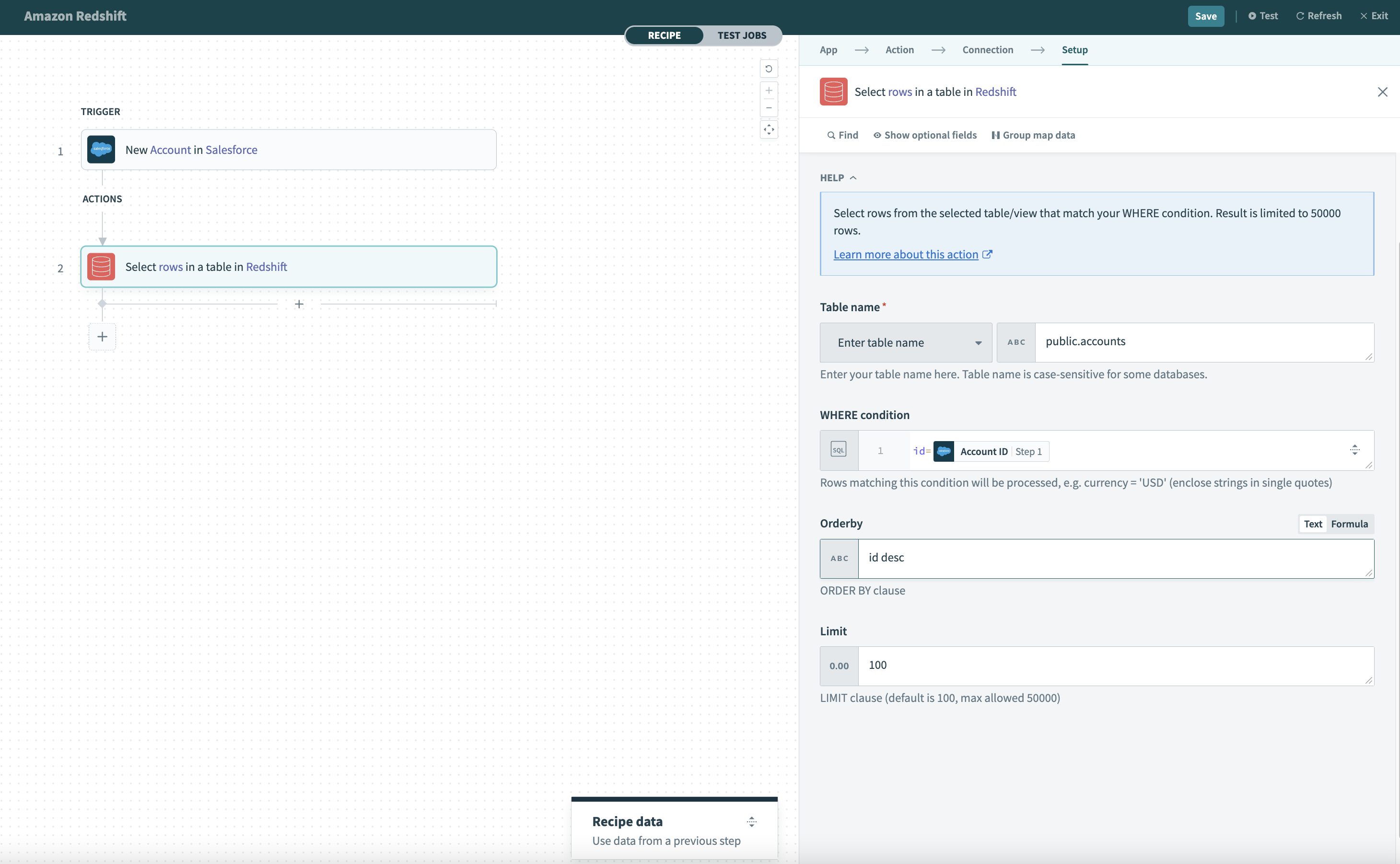
# Order by
Rows returned from this action can be ordered based on the Order by input field. This field is used to change the default ordering of rows from your Redshift database.
You can also define the direction of order for each column you wish to order by. The following order by statement will order rows by priority in ascending order followed by created_date in descending order (latest first).
priority asc, created_date desc
 Sorting select action results with Order by
Sorting select action results with Order by
# Limit
This input field determines the maximum number of rows to return. The default limit is 100 and the maximum is 50,000 rows for a single Select rows action.
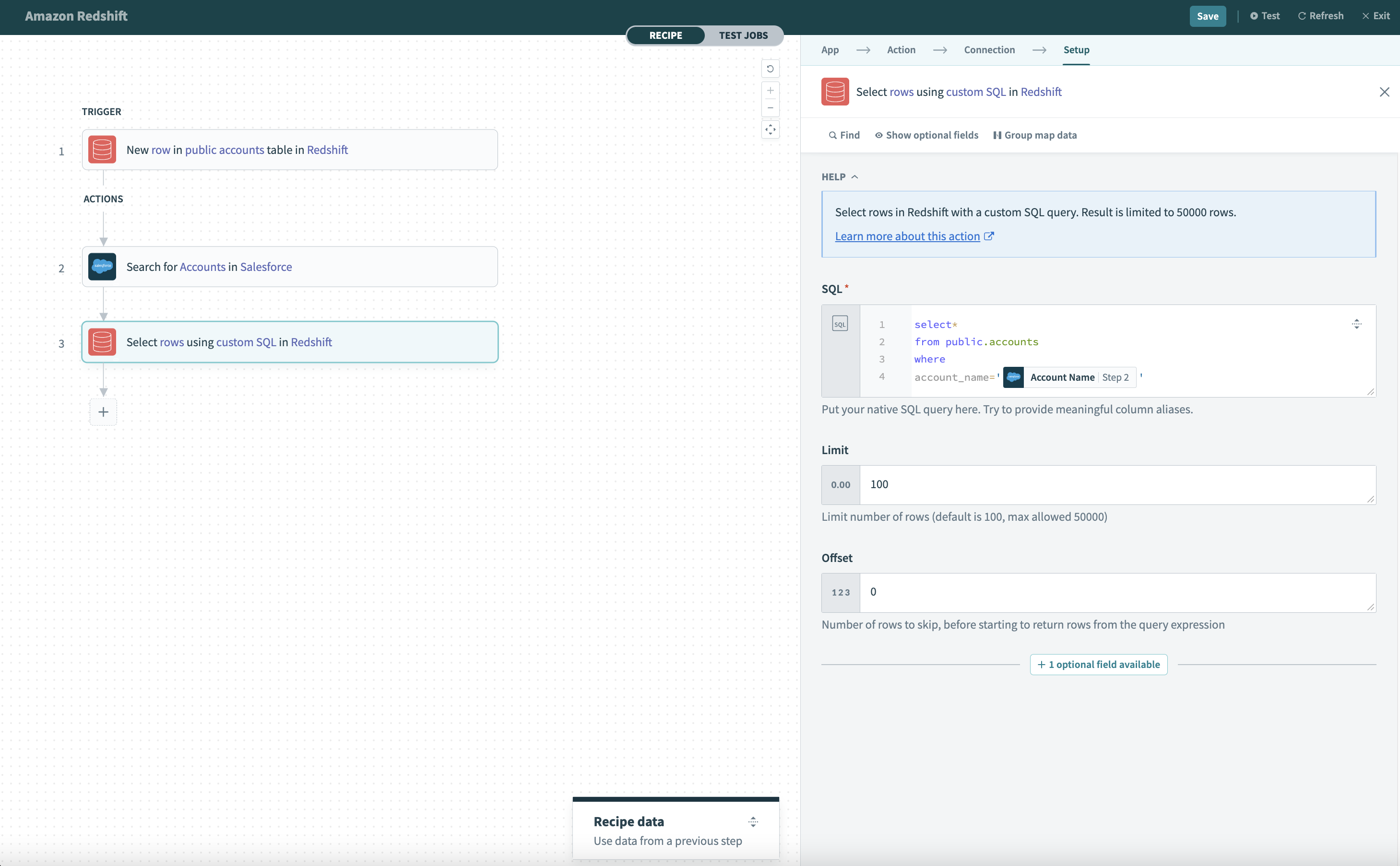
# Select rows using custom SQL
This action lets you select rows based on a custom SQL query. Rows that are returned from the query will be returned as the output of this action.
 Select rows using custom SQL action
Select rows using custom SQL action
50,000 RECORD LIMIT
Starting February 8, 2026, the Select rows using custom SQL action returns a maximum of 50,000 records for all new recipes and existing recipes that don't currently exceed this limit. Starting March 15, 2026, this limit extends to all recipes using this action, including existing recipes that currently exceed the limit.
Recipes configured to retrieve more than 50,000 records will be truncated to this limit.
This change improves platform reliability and performance while preventing large queries from overloading database connections or impacting upstream systems.
# SQL
Provide the SQL to be executed to select rows. The SQL here will be used to generate the output datatree. To do this, the SQL will be executed once when you provide it. You can map datapills here to execute dynamically changing SQL statements. Remember to wrap datapills in quotes ('').
Avoid using limit clauses like LIMIT in your SQL. This is because the limit to the number of rows returned in the query is based on the value defined in the Limit input field. Adding your own limit clause will cause the action to fail.
# Limit
This input field determines the maximum number of rows to return. The default limit is 100 and the maximum is 50,000 rows for a single Select rows using custom SQL action.
If this field is left blank, LIMIT 100 will be used.
# Offset
This input field gives you the option to fetch only a page of results from the entire results set. For example, to skip the first 100 rows of the selected results set, input 100 to this field. The default is 0.
Last updated: 2/5/2026, 7:58:44 PM