# Block kit in modals
Modals allow you to build rich, interactive, and dynamic views that collect information from users in a structured manner. This is done by using the Open/update or push modal view action.
 Block kit modal example
Block kit modal example
Modals views are built using blocks. A modal view has a title, the view (comprised of blocks), and submit/close buttons. You can also use modal-only blocks called input blocks. These are:
- Single-line input
- Multi-line input
- Select menu input
- Datepicker input
- Checkboxes input
# Interactive components compared to input blocks
Input blocks work differently from the interactive components of other blocks.
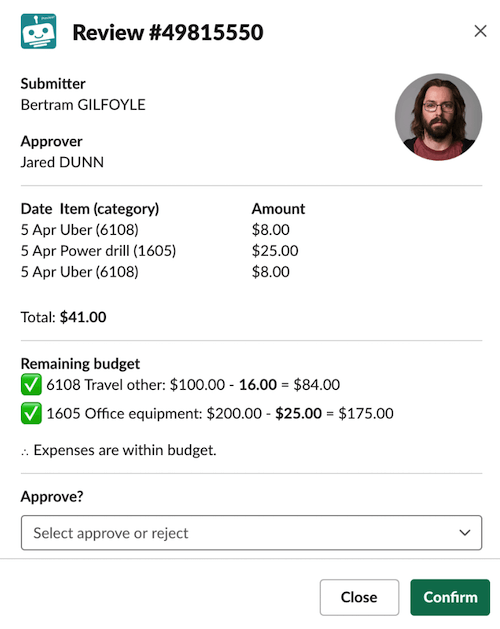
Buttons, menus, and other interactive components invoke commands when clicked. In contrast, input blocks only invoke commands when a view is submitted. For example, in a modal, a user can choose to Approve or Reject. The value only locks in after they submit the modal by clicking the Submit button.
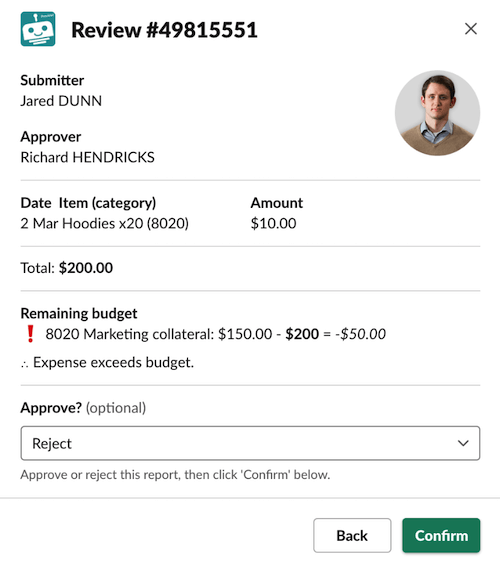 The user's choice is only locked in after clicking submit
The user's choice is only locked in after clicking submit
If a view contains input blocks, you must define the submit and close buttons. If it does not contain input blocks, then it is not necessary to include submit and close buttons.
# Modal stack
A modal can hold up to three views simultaneously in a view stack. Users only see the top-most view, called the active view. View stacks are useful because they enable the user to return to previous views after submitting or closing their active views.
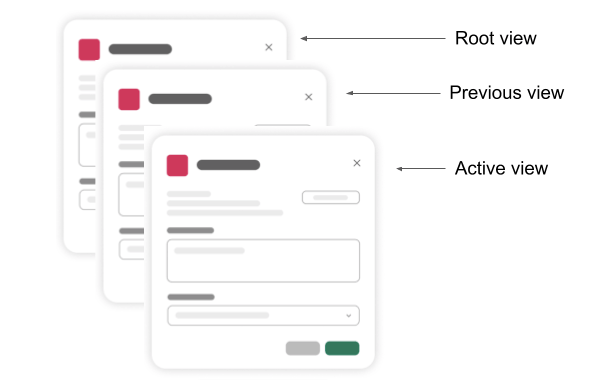 Each modal can stack up to three views
Each modal can stack up to three views
Opening a modal opens in the root view. Updating a modal replaces an existing view you specify (through its View ID), while pushing a modal view applies a new view on top of the view stack.
Each view has an associated view ID. This view ID is required to update an existing view.
# Passing information between views
When users interact with interactive components or submit modals, a bot command triggers a downstream recipe. This downstream recipe can update or push modal views. To ensure the modal actions in the downstream recipe have the necessary context, pass parameters such as User ID or Opportunity ID.
In modals, these values are called Command input values. They allow you to pass specific data from one part of a recipe to another. For example, if a user selects an account in a modal and you define the account_id as a Command input value, you can pass it to subsequent actions to update or retrieve information about that account. This enables dynamic and interactive workflows, such as generating dynamic picklists based on user input.
To pass these parameters, you must define them in the New command trigger in the downstream recipe. It is crucial to ensure that the parameter names and data types match their upstream counterparts. For example, if you use opportunity_id as a single line input in the view of a modal (rendered in an upstream recipe), you must also specify opportunity_id as a string parameter in the New command of the downstream recipe.
You can pass parameters using JSON, for example, {"opportunity_id": "OPP1234567"} or {"OpportunityId": "OPP1234567"}. Command input values also support passing JSON arrays and objects as parameters.
For example, you can pass an array of user IDs:
{
"user_ids": ["USER123", "USER456", "USER789"]
}
You can also pass an object with key-value pairs that describe an opportunity:
{
"opportunity": {
"id": "OPP1234567",
"name": "New business opportunity",
"amount": 50000,
"status": "Open"
}
}
CHARACTER LIMITATIONS
Modals don't support CamelCase characters or comma-separated name-value pairs as Command input values. However, CamelCase is supported in JSON, for example, {"OpportunityId": "OPP1234567"}.
# Working with modals
You can use the following components to open modals:
- Buttons
- Menus
- Overflow
- Select menus
- Datepickers
- Radio buttons
- Shortcuts
- Message actions
- Slash commands
- Modal view submissions
The preceding components invoke a bot command and generate a Trigger ID, which the New command trigger picks up. A Trigger ID is mandatory for all types of modals. Opening, updating, and pushing modal views all require this Trigger ID.
The New command trigger datatree contains a Modals object that stores modal-related context, enabling you to perform modal actions.
| Modal datapills | Description |
|---|---|
| View ID | View ID of view from which command was invoked, a.k.a. the active view. If the command was invoked from a view submission, then this view ID cannot be used for updating/pushing views as the view has already closed on submission. If only 1 view is active, then this view ID will be identical to the root view ID. |
| Root View ID | View ID of the root view. |
| Previous View ID | View ID of the view beneath the current view |
| Private metadata | Private data you can optionally use to pass to downstream recipes. This field is encrypted and hidden from users. |
| Hash | A unique value you can optionally use when updating modals. When provided, the hash is validated such that only the most recent view is updated, ensuring the correct view is being updated when updates are happening asynchronously. |
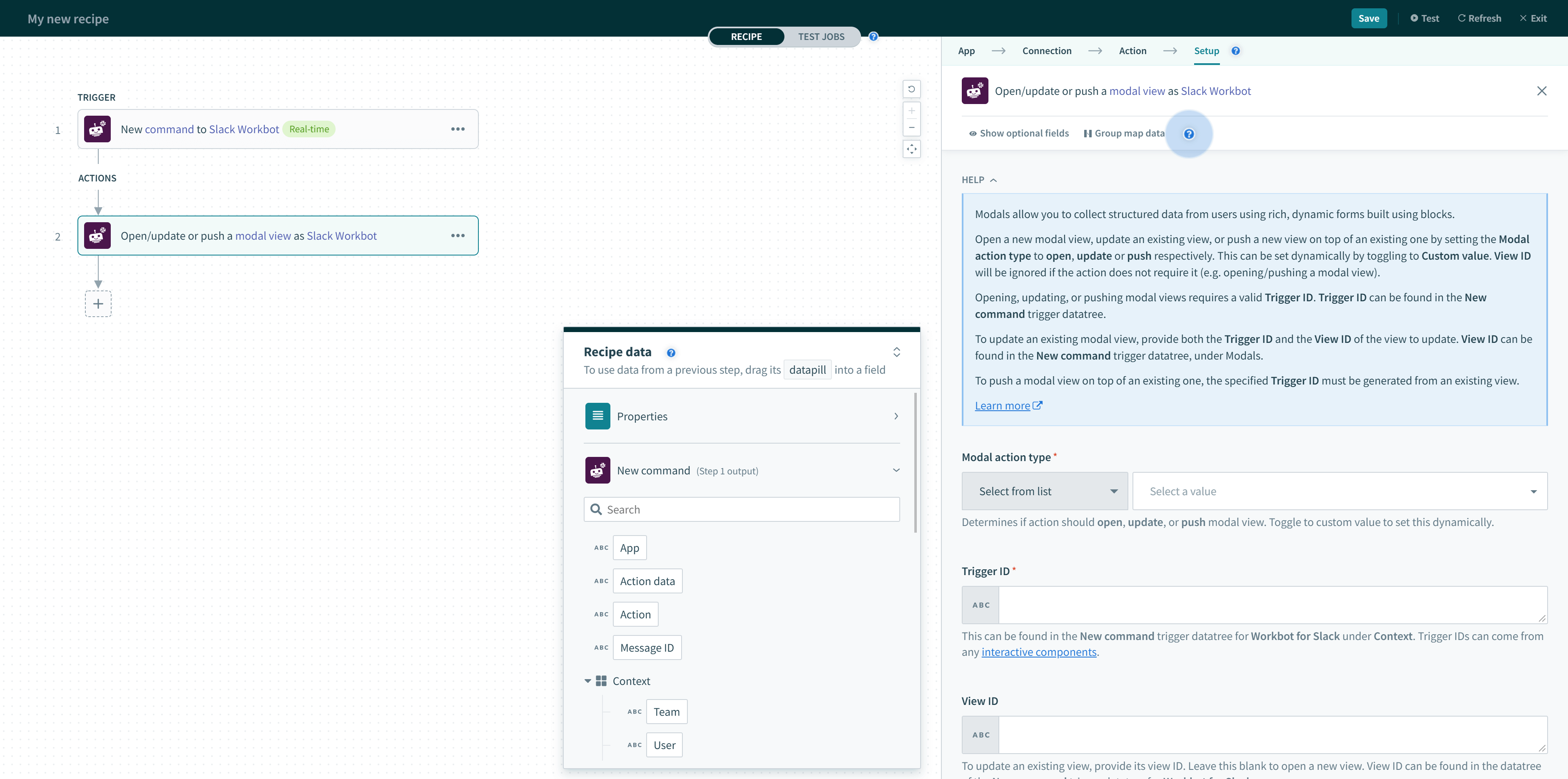
# Open/update or push modal view action
This action allows you to build rich, interactive, and dynamic modals that collect information from users in a structured manner. Modals are built using blocks.
 Open/update or push modal view action
Open/update or push modal view action
You can open a new modal view, update an existing view, or push a new view on top of an existing one by setting the Modal action type to open, update, or push.
For all modal action types, a Trigger ID is required. Slack generates trigger IDs when users interact with the following components:
- Buttons
- Menus
- Overflow
- Select menus
- Datepickers
- Radio buttons
- Shortcuts
- Message actions
- Slash commands
- Modal view submissions
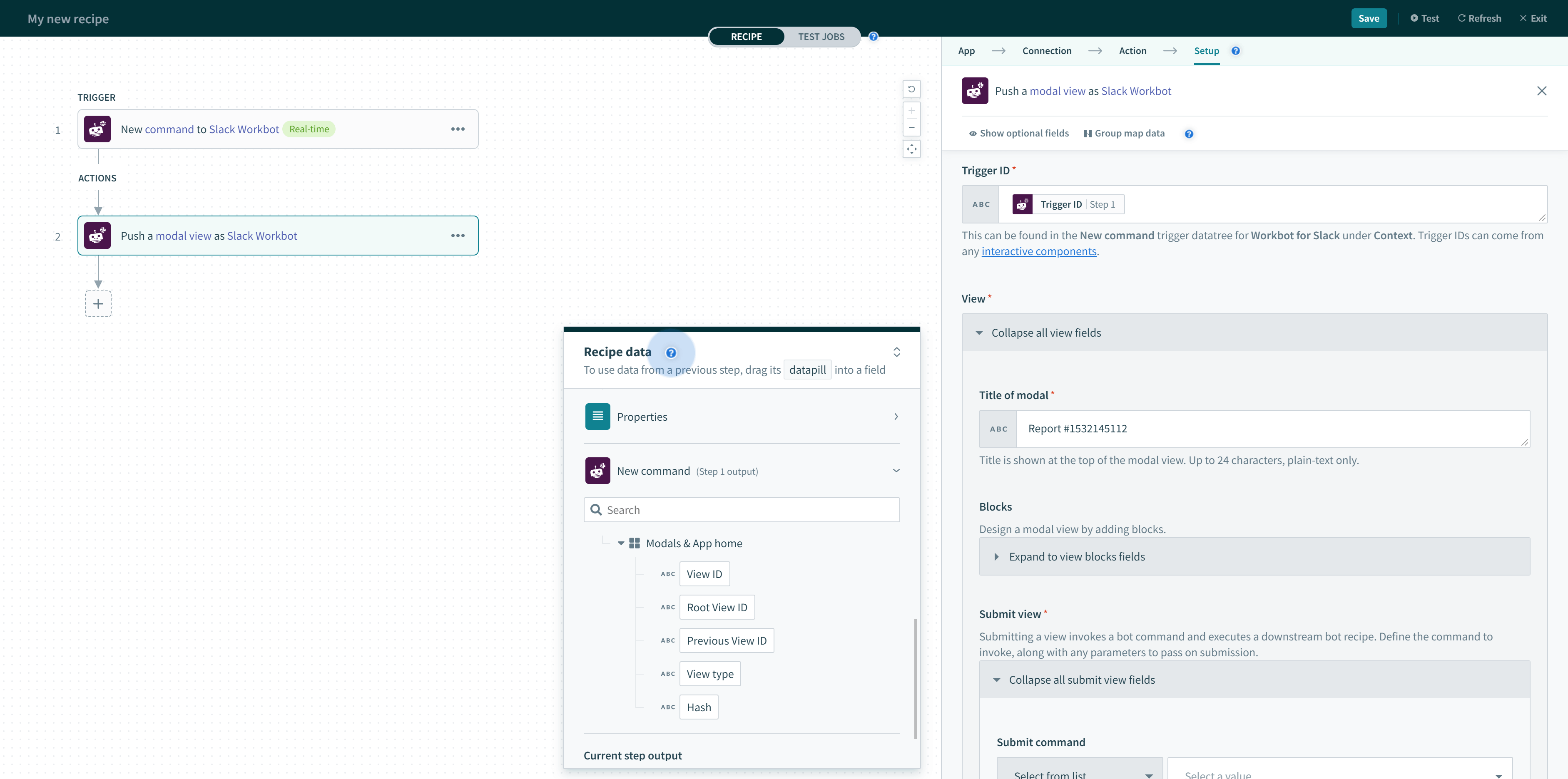
To open a modal view, map the Trigger ID Step 1 datapill from the output of the New command trigger.
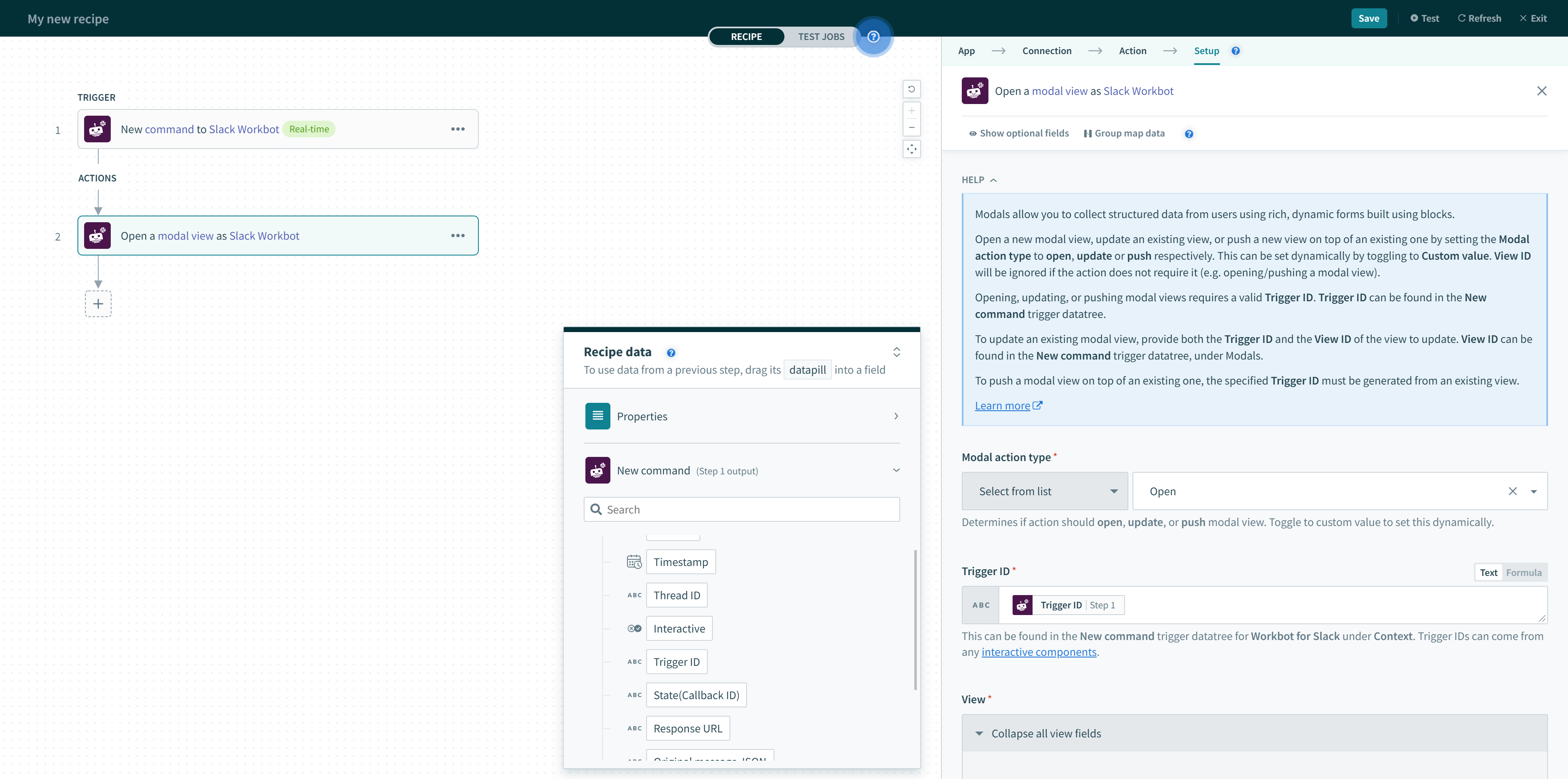 Trigger ID for opening modal views (found in the New command trigger)
Trigger ID for opening modal views (found in the New command trigger)
Updating a modal view also requires Trigger ID, but you must also specify the View ID of the view to update. This View ID can also be found in the New command trigger datatree, under Modals.
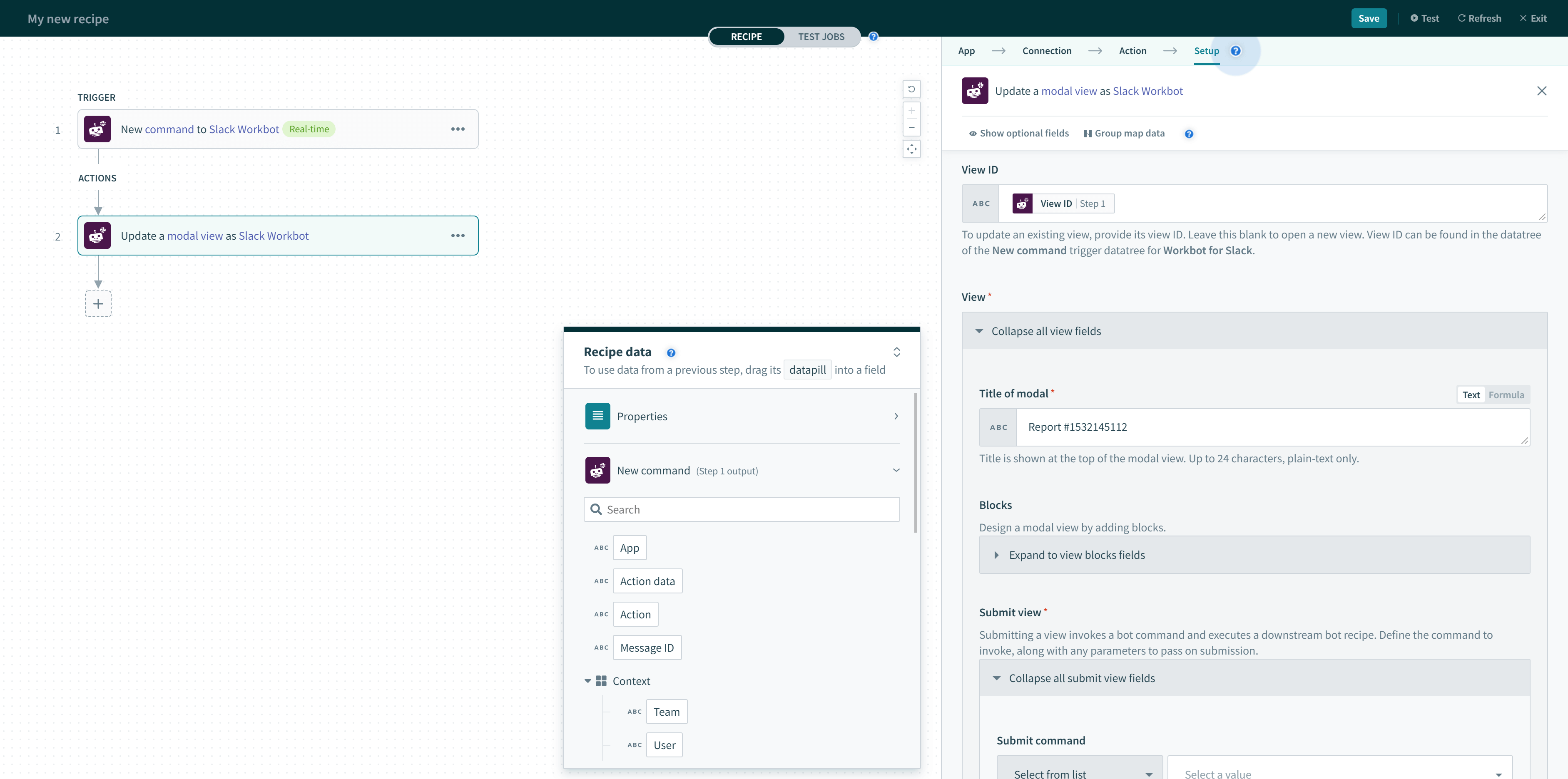 Trigger ID and View ID (both found in New command trigger) for updating modal views
Trigger ID and View ID (both found in New command trigger) for updating modal views
Pushing a modal view (on top of an existing one) requires Trigger ID. However, this Trigger ID must be generated from an existing view.
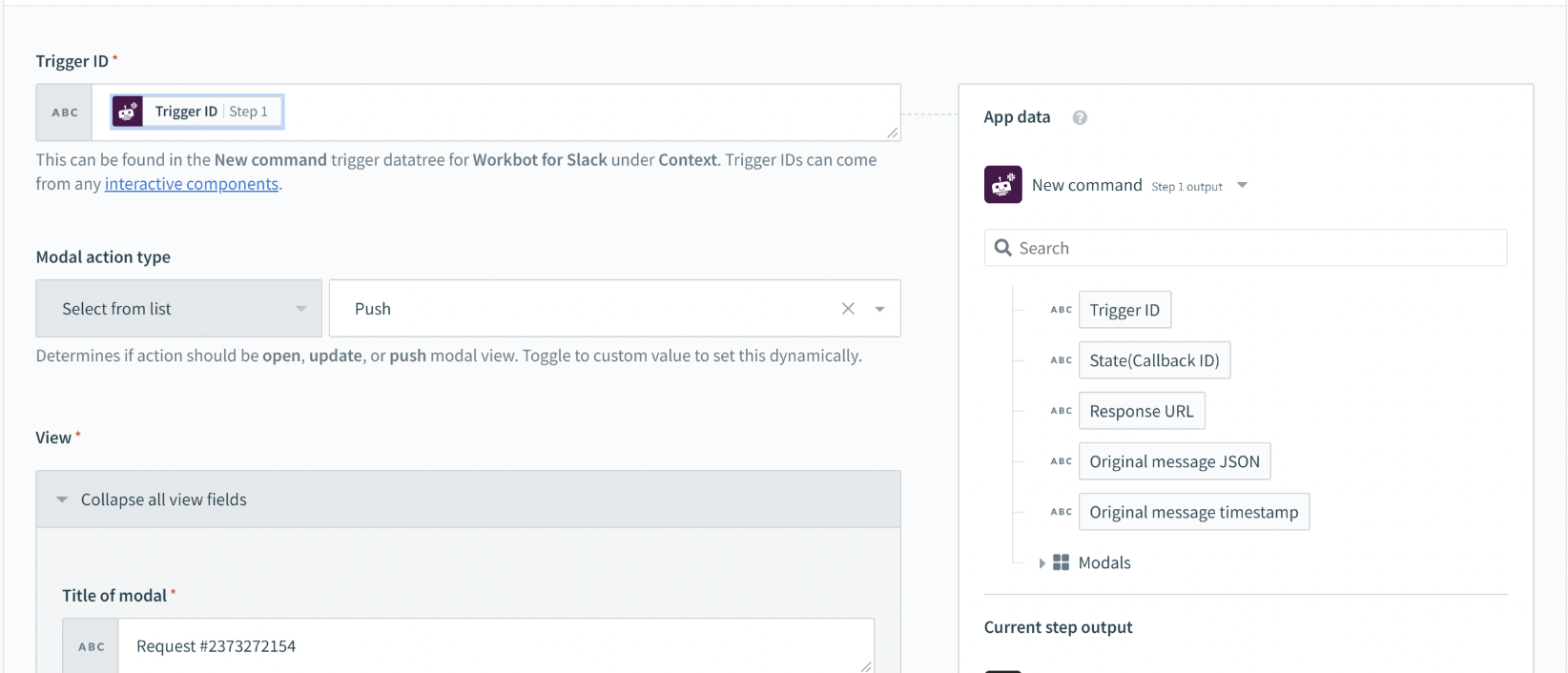 Trigger ID for pushing modal views (found in New command trigger)
Trigger ID for pushing modal views (found in New command trigger)
# When to update modal views
Typically, bot commands update the active view in which they exist using the View ID.
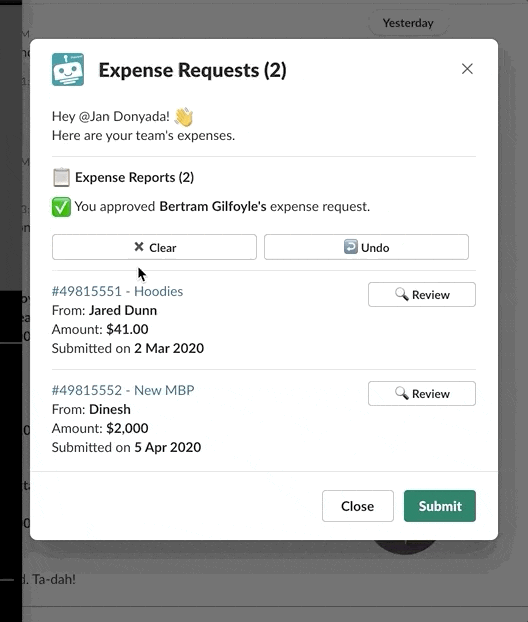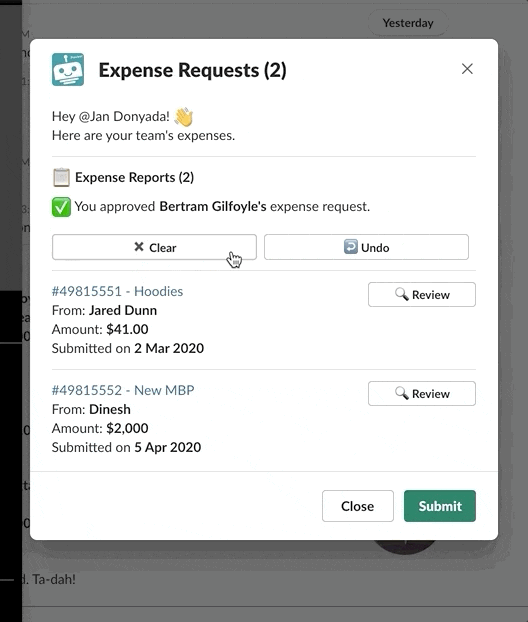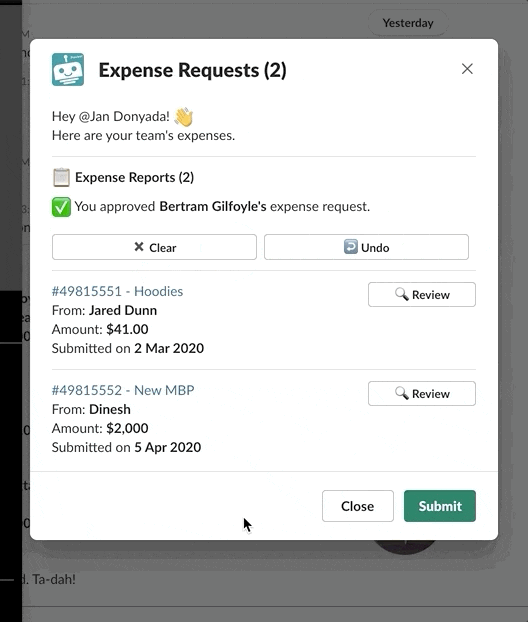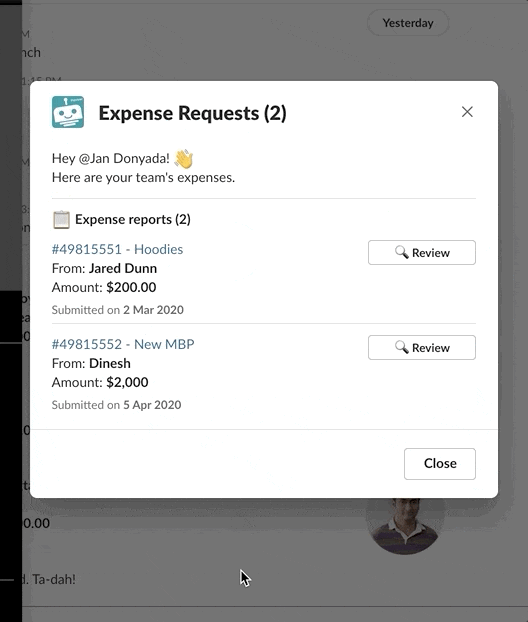 Making changes on the active view
Making changes on the active view
In contrast, modal submissions typically update the root view (Root View ID) or the previous view (Previous View ID). You can find these views in the New command trigger's datatree within Modals.
 Root View ID and Previous View ID found in the New command trigger
Root View ID and Previous View ID found in the New command trigger
SUBMITTING A VIEW
When a view is submitted, it closes by default. Use the correct View ID when updating views in response to view submissions.
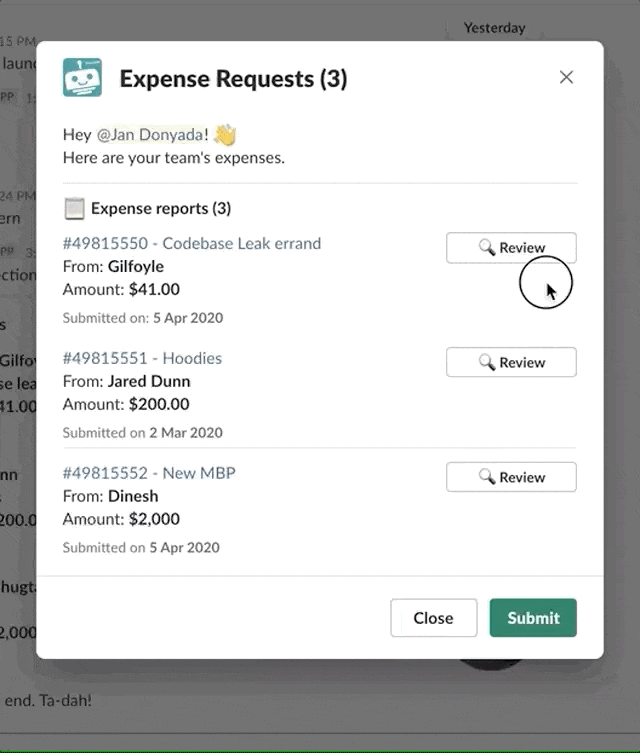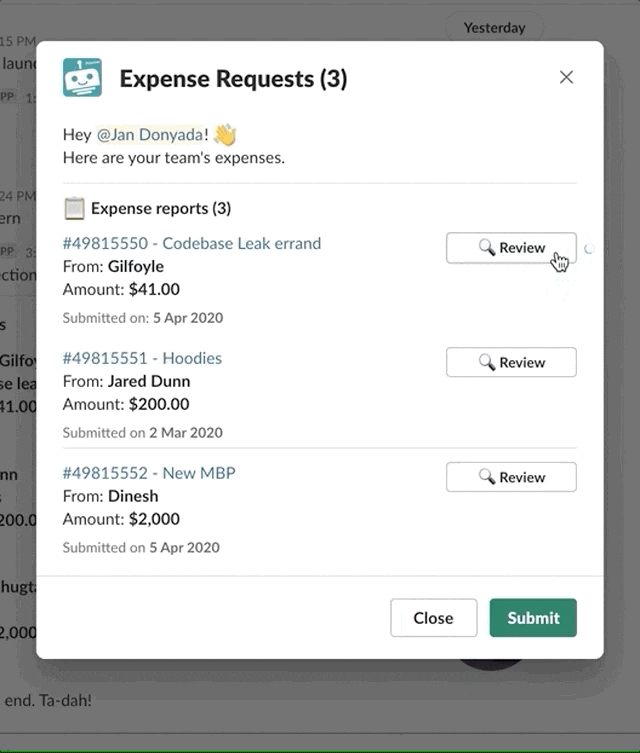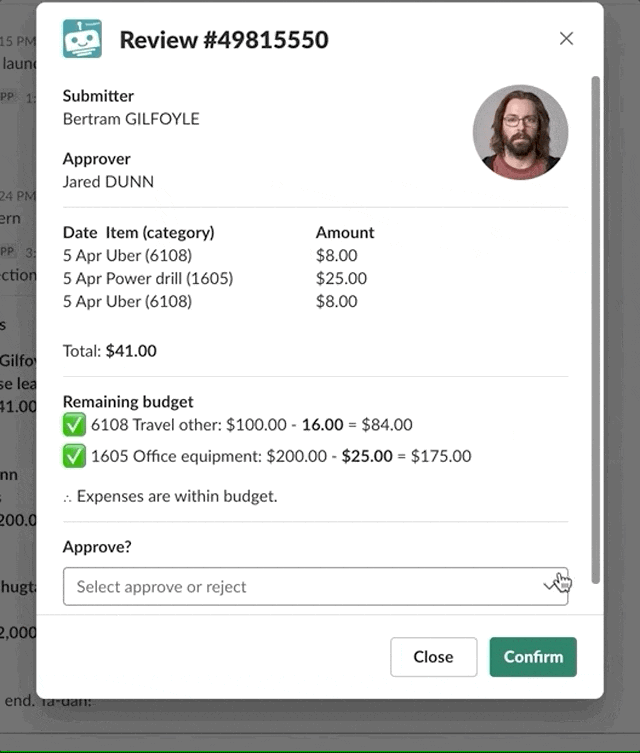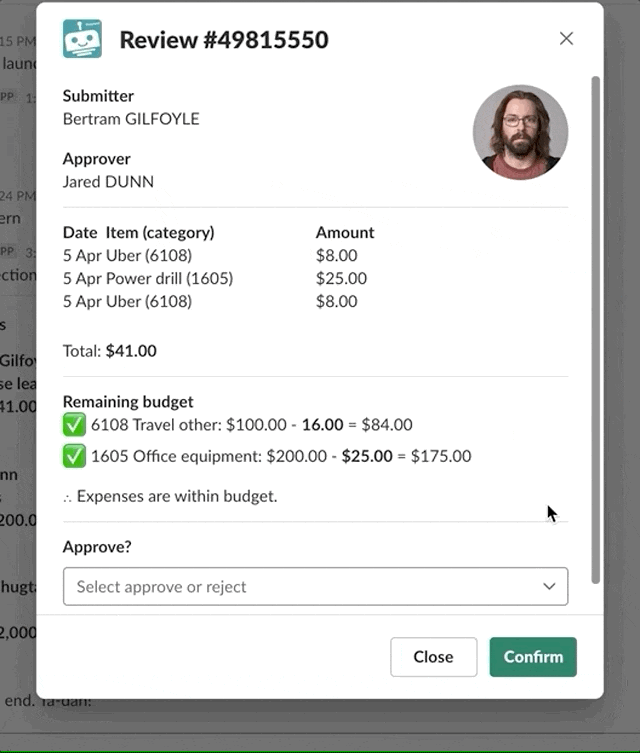
# When to push modal views
Typically, bot commands push views on top of the active view in which they exist using the View ID. You can find the View ID in the New command trigger's datatree within Modals.
 Making changes on the active view
Making changes on the active view
 Root View ID and Previous View ID found in the New command trigger
Root View ID and Previous View ID found in the New command trigger
SUBMITTING A VIEW
When a view is submitted, it closes by default. Ensure you only push a modal view on top of an active view.
# Open/update or push modal view action input
The following table describes the configuration when using this action:
| Input | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Trigger ID (required) | Modal views can only be opened by interactive components (like buttons & menus), modal submissions, message actions, shortcuts, and slash commands. When users interact with or use these features, a trigger ID is generated. You can grab these from the New command trigger datatree under the Modals object. | ||
| Modal action type (required) | You can open a new modal view, update an existing view, or push a new view on top of an existing one by setting the Modal action type to open, update or push respectively. This can be set dynamically by toggling to Custom value. View ID will be ignored if the action does not require it (for example, when opening or pushing a modal view). | ||
| View ID (optional) | To update an existing modal, specify the view ID of the view you want to update. This field is ignored when opening or pushing modal views. | ||
| View | Title of modal | Title of the modal view. Up to 24 characters only. | |
| Blocks | An array of blocks you can stack and rearrange. | ||
| Submit view | Submit command | Command to invoke when users do a modal submission. | |
| Command input values |
When users submit modals, you may need to pass parameters such as a User ID or Opportunity ID, to give context to the downstream recipe. You must define these parameters in the modal and pass them to the New command trigger in the downstream recipe to prepare for receiving them. The parameter names in both the upstream recipe containing the modal and the downstream recipe with the New command trigger must match. Use JSON to pass parameters in modals, as the action does not support comma-separated name-value pairs or CamelCase. For example, {"opportunity_id": "OPP1234567"}. However, CamelCase parameters are supported within JSON, for example, {"OpportunityId": "OPP1234567"}. You can also pass arrays or objects using JSON.Ensure the parameter names and data types match their upstream counterparts. For example, when using opportunity_id as a single line input in a modal view (rendered in an upstream recipe), also specify opportunity_id as a string parameter in the New command trigger of the downstream recipe.
| ||
| Submit button label | Label of the submit button. Up to 24 characters only. | ||
| Close button label | Label of the close button. Up to 24 characters only. | ||
| Clear on close | Clicking on the close button will clear all views in a modal and close it. Defaults to false. | ||
| Notify on close |
Sends a view_closed event when a user clicks the close button. Defaults to false. Use the New event trigger to listen to this event.
| ||
| Advanced | Private metadata | For advanced users. Used to pass sensitive data. This field is encrypted and hidden to users. Max length of 3000 characters. | |
| Callback ID | For advanced users. Used to reference the view submission event in downstream recipes. Max length of 255 characters. | ||
| Hash | A unique value you can optionally use when updating modals. When provided, the hash is validated such that only the most recent view is updated, ensuring the correct view is being updated when updates are happening asynchronously. This field is ignored when opening or pushing modal views. | ||
Last updated: 5/21/2025, 5:22:32 AM