# Customizing user interfaces for OpenAPI connectors
In addition to universal connectivity, the OpenAPI connector also allows you to customize its user interface in Workato for the best user experience.
In this guide, we'll show you how to:
- Customize object names and hints
- Customize how API operations are grouped into actions
- Hide action input fields
- Customize the connector's application name
# Best practices
When customizing the user interface of an OpenAPI connector, we recommend following these best practices:
Verify object hints are present and accurate. Ensuring information is easy to access and understand will help your users get up and running quickly.
If you have the ability to directly edit your Swagger file, add object hints and external links if needed.
If building a custom connector, replace OpenAPI with your application's name.
Test, test, test! Whether you're developing a custom connector or customizing the interface for a standard OpenAPI connector, make sure to iteratively test your changes. Identifying an issue is easier if you test one change at a time.
# Customizing objects
Details about objects are automatically extracted from endpoint fields. In this section, we'll cover:
- Choosing the object name field
- Customizing object hints and links
- Substitution rules for object names and hints
- Using Static object names to map user-friendly display names for objects and operations
# Example endpoint
The examples in this article will use the following endpoint:
/* swagger-petstore-1-1.json */
{
"paths":{
"/pet":{
"post":{
"tags":[
"pet"
],
"summary":"Create a new pet",
"description":"Add a new pet to the store. [More information](https://app.swaggerhub.com/apis/Colon-Org/Swagger-PetStore-3.0/1.1)",
"operationId":"createPet",
"requestBody":{
"description":"Add a new pet to the store",
"content":{ ... },
"required":true
}
}
}
}
}
# Customizing object names
Object names refer to the types of records an API interacts with, such as pet or user. In the Recipe Editor, users can select the type of object an action interacts with:
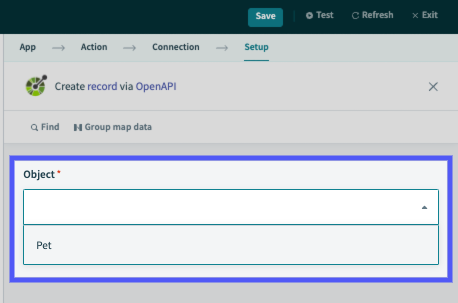 Picklist of which object to operate on
Picklist of which object to operate on
Objects names are derived from the object's summary, description, or operationId field. When setting up the connection, users are prompted to select one of these options in the Object name field.
Connection setup: Select the object name field
If summary is chosen, the object name will be based on "Create a new pet", (view example endpoint). After excluded words are removed (such as a or and), the resulting object name will be Pet.
Note: You can hard-code the object name field if developing a custom connector. Refer to the Using The OpenAPI Connector To Create Custom Connectors guide for more info.
However, we recommend directly editing the Swagger file instead.
# Customizing object hints and links
Object hints are short, helpful descriptions that display below the object picker field:
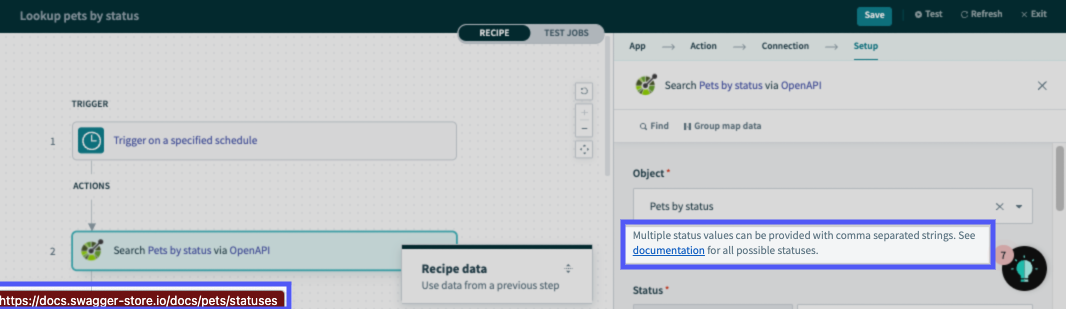 Object hints
Object hints
Users can use an object's summary or description field as the object name by default. When setting up the connection, users are prompted to select one of these options in the Object hint field.
If description is chosen, the object hint will be "Add a new pet to the store. More information (opens new window)", (view example endpoint).
EXTERNAL LINK FORMAT
External links in object field hints must adhere to one of the following formats:
- Standard links, which contains the full URL and is typically formatted as
[link text](url). For example:[Workato](https://www.workato.com). These types of links are rendered as-is and don't require any configuration. - Categorized relative links, formatted as
[link text](key:path). Thekeyreferences a base URL that, when combined with thepath, creates a full URL. For example:- Base URL:
https://docs.swagger-store.io/docs/ - Path:
pets/statuses - Full URL:
https://docs.swagger-store.io/docs/pets/statuses
- Base URL:
# Adding a base URL
In the following example, set up the key of "doc":
/* swagger-petstore-1-1.json */
{
...
"description":"Multiple status values can be provided with comma separated strings. See [documentation](doc:pets/statuses) for all possible statuses."
...
}
You will need to supply the base URL (https://docs.swagger-store.io/docs/) to complete the helplink.
Configure the External documentation links connection fields in Workato:
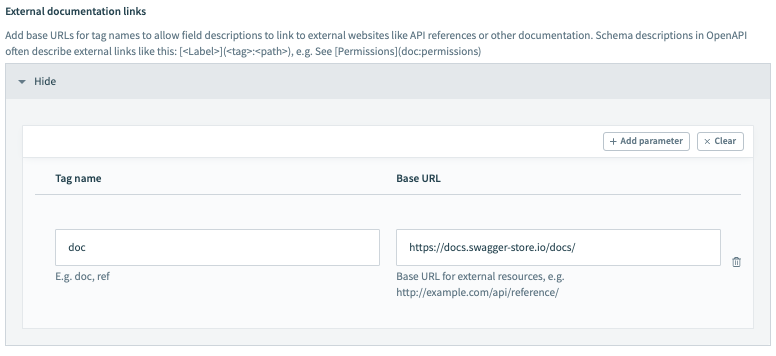 Connection setup: External documentation links
Connection setup: External documentation links
Note: You can hard-code the object hint field if developing a custom connector. Refer to the Using the OpenAPI connector to create custom connectors guide for more info.
However, we recommend directly editing the Swagger file instead.
# Using substitution rules
In some cases, removing filler words and keywords from object names and hints doesn't lead to the best results.
Let's say we're working with object names and want to use the summary field for extraction. The object's summary is "Allows users to create a pet".
If only filler words and keywords are removed, the result will be Allows users to pet - definitely not an ideal result.
You can modify extracted values before keywords and filler words are removed using the Object name substitutions and Object hint substitutions fields.
The table below demonstrates how a substitution rule that strips Allows users to from Allows users to create a pet would improve the final result:
| Description | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Input |
Value is extracted from the object's summary field
|
Allows users to create a pet
|
| Pattern |
Uses capture group to extract characters after Allows users to |
Allows users to (.+)
|
| Replacement |
Replaces value with results of first capture group ( (.+) )
|
\1
|
| Substitution result | Value after applying the substitution rule |
Create a pet
|
| Final result |
Final object name after removing filler words (a, the, etc.) and known words (ex: Create) from Substitution result |
Pet
|
NOTE
When multiple substitution rules are present:
pattern
Additionally, some hints contain relative links to external sites.
# Static object names
If the OpenAPI spec does not provide user-friendly names for individual API endpoints, use Status object names to map descriptive display names for eat object and operation.
To remap the operation in the example endpoint, we will provide a display name for the "Create a new Pet" ("operationID": "createPet").
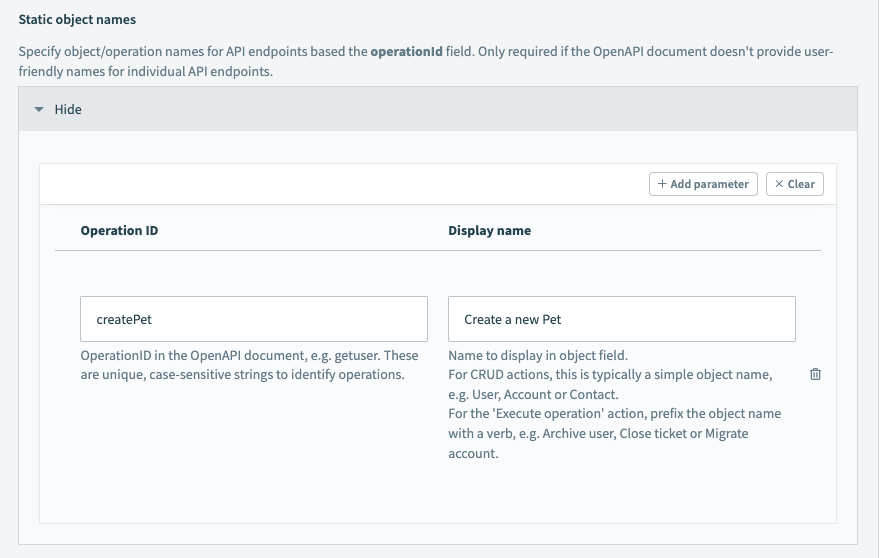 Connection setup: Adding a static object name
Connection setup: Adding a static object name
# Customizing API operation grouping
- Understanding API operation assignment
- Default API operation grouping rules
- Substitution rules for API operations
# Understanding API operation assignment
The OpenAPI connector contains a set of default rules for grouping API operations into recipe actions. These rules also control the objects displayed in the object picker when setting up an action.
The following image demonstrates how two API operations from a Swagger file would map to actions in the Recipe Editor:
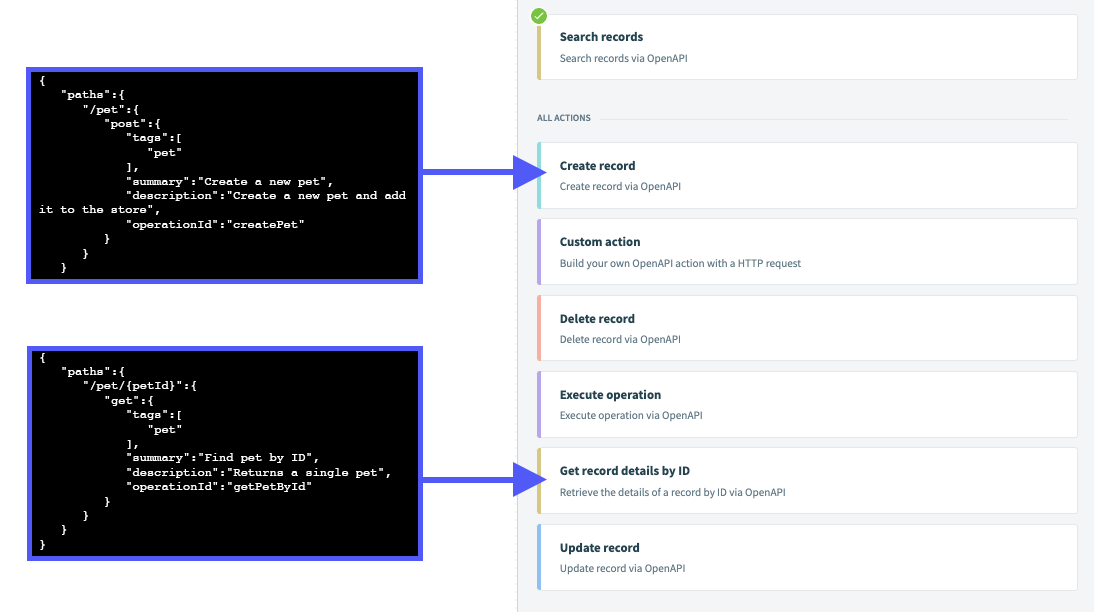
MISSING SOME API OPERATIONS?
If an action doesn't contain an API operation you expect it to, look for it in the Execute operation action.
If an API operation can't be matched, the connector will group the operation under this 'fallback' action. Refer to the Default operation grouping rules section below for more info.
Grouping rules are based on two factors:
Keywords in the API operation's summary and operation ID. When the connector parses the Swagger file to create recipe actions, it's also checking for keywords in the API operation's
summaryandoperationIdfields. The connector uses these keywords to assign operations to recipe actions.For example, an operation ID of
createPetwould assign the operation to the Create record action. This is because the operation ID contains the wordcreate.The operation's HTTP method, which is specified in the Swagger file. HTTP methods describe the type of action an operation performs for a given object, such as
create(usuallyPOST) or search (GET).For example, operations that use the
GETmethod would be assigned to either the Search records or Get record details by ID action.To disable this grouping method, set the Use HTTP method semantics for grouping operations field to No when setting up the connection. This can be useful if an API doesn't follow REST standards. For example, every endpoint uses the
POSTmethod.
# Default API operation grouping rules
The following table details the default operation grouping rules for OpenAPI connectors. The table columns are as follows:
Name and description: The name and description of the action
Operation keywords: The keyword(s) the connector uses to perform API operation grouping. If an API operation's
summaryoroperationIdcontains these keywords, it will be mapped to this action in the Recipe Editor.For example: If a
summaryoroperationIdcontainsaddoradds, the API operation will be assigned to the Create record action.HTTP methods: If the Use HTTP method semantics for grouping operations option is enabled, the connector will match the methods list to this action.
For example: If an operation uses the
POSTmethod, it will be assigned to the Create record and Update record actions.
| Name and description | Operation keywords | HTTP methods |
|---|---|---|
| Create record Creates a new record of a specified object type. For example, if a |
| POST, PUT |
| Update record Updates an existing record using its unique identifier. |
| PUT, POST, PATCH |
| Search records Searches for records of a specified object type. |
| GET |
| Get record details by ID Retrieves a record using its unique identifier. |
| GET |
| Delete record |
| DELETE |
| Execute operation This action is considered a 'fallback'. If an API operation can't be matched to a specific action, it will be grouped under this action. | POST, PUT, GET, DELETE, PATCH |
# Substitution rules for API operations
If operation IDs in your Swagger file aren't as simple as createPet or searchPets, you can use substitution rules to improve or customize API operation grouping.
# How to apply substitution rules
Substitution rules are applied to the specified fields before the grouping logic. If a field contains certain patterns that do not align with your planned grouping, you can create rules to replace them with preferred terminology or structure.
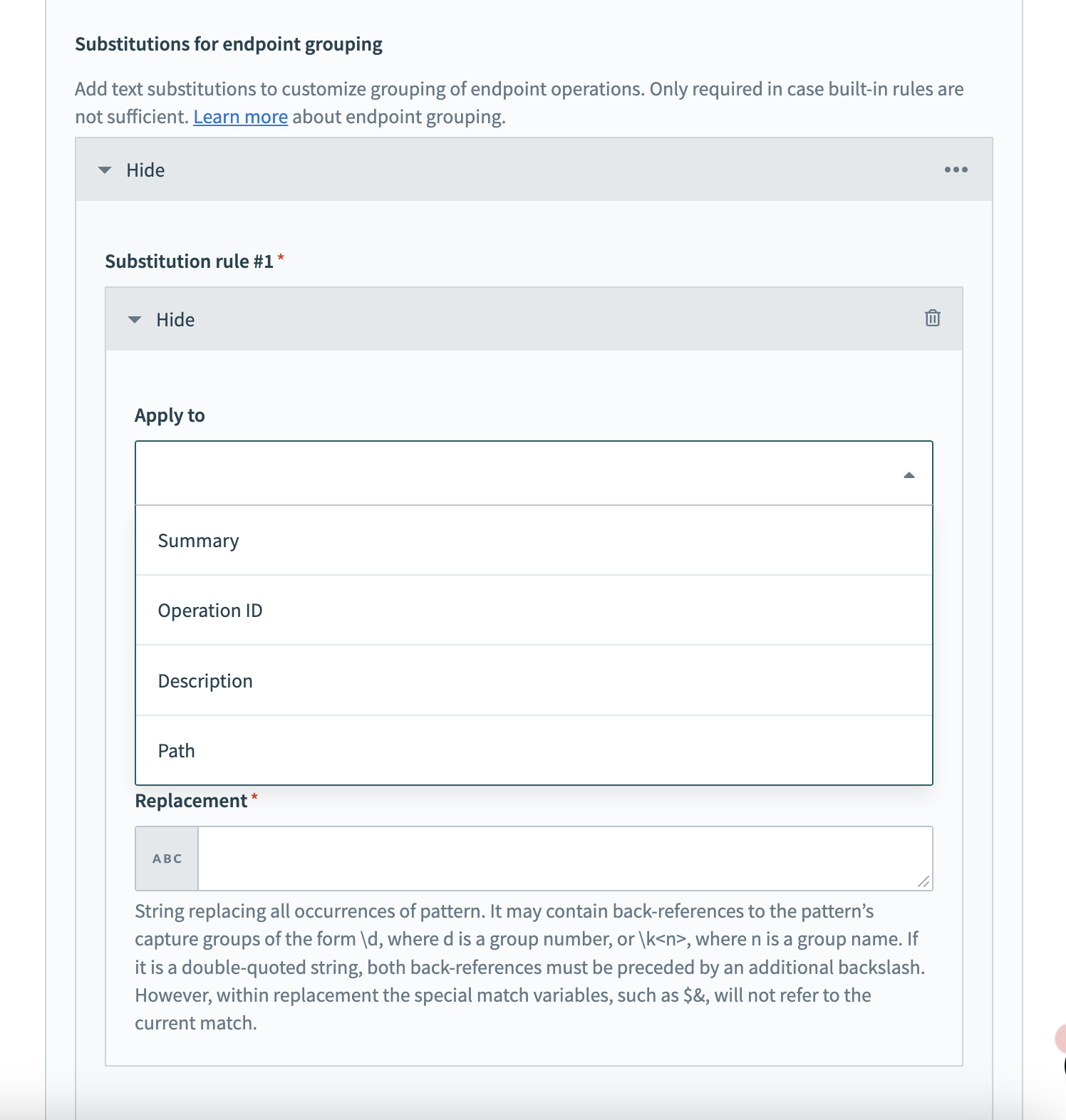 Apply substitution rules to API operation details
Apply substitution rules to API operation details
To apply substitution rules fill in the following fields in Workato:
- Apply to
- Select the part of the API operation detail you plan the rule to affect. You can choose from
Operation ID,Summary,Description, andPath.
- Pattern
- Enter the regular expression pattern that identifies the text you plan to change.
- Replacement
- Provide the new text that replaces the identified pattern.
The following table demonstrates how a substitution rule transforms an operation ID of operation-8452/pet-create to create-pet:
| Description | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Input |
Value is extracted from object's operationId field
|
operation-8452/pet-create
|
| Pattern |
Uses capture groups to extract the object (pet) and verb (create) of the operation ID
|
operation-8452/(?<object>.+)-(?<verb>.+)
|
| Replacement | Replaces value with results of the capture groups |
\2-\1
|
| Final result | Final operation ID after applying the substitution rule |
create-pet
|
The connector can now assign the API operation to the Create record action with an improved operation ID of create-pet.
NOTE
When multiple substitution rules are present:
pattern
# String substitutions
String substitutions precede the application of built-in keyword rules. These substitutions modify the operation's summary, operationId, description, and path to ensure endpoint attributes match the expected keywords for action mapping.
The following table details the operation grouping rules for OpenAPI connectors after string substitutions:
| Action type | Operation keywords | HTTP methods | Special conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create record |
| POST, PUT | - |
| Update record |
| PUT, POST, PATCH | - |
| Search records |
| GET | Must not have an id, ids, or <record_id_field_name> request parameter. Must have a response field of type array. |
| Get record details by ID |
| GET | Must have an id, ids, or <record_id_field_name> request parameter. Must not be prefixed with Search records action keywords. |
| Delete record |
| DELETE | - |
# New/update trigger requirements
For the New/update trigger to correctly identify relevant API operations, each operation must meet the following conditions:
- Satisfy search records action criteria: Aligns with the requirements set for the Search records action.
- Timestamp request parameter: Includes a timestamp request parameter, typically named
update,change,modify,time,stamp,since, orstart. - Timestamp in response: Features a timestamp field in the response, recording the last update time. Common field names are
update,change,create,modify,modified,time, orstamp. - Identifier in response: Contains an identifier field in the response, typically named
idorname.
# HTTP method-based grouping
The use_operation_names_for_grouping setting in the OpenAPI connector determines how HTTP methods influence operation grouping.
When this setting is enabled, the following rules are applied based on their HTTP methods:
- Create record action: Assigns an endpoint if the HTTP method is POST or PUT.
- Update record action: Assigns an endpoint if the HTTP method is POST or PUT.
- Delete record action: Assigns an endpoint if the HTTP method is DELETE.
- Search records action: Assigns an endpoint if the HTTP method is GET.
- Get record details by ID action: Assigns an endpoint if the HTTP method is GET, provided the operation doesn't qualify for the Search records action.
- Execute operation action: Assigns an endpoint if it doesn't fit into the Search records, Create record, Update record, Get record details by ID, or Delete record actions.
- New/update trigger: Assigns an endpoint if the HTTP method is GET.
When this setting is disabled, the following rules are applied for operation grouping:
- Update record action: Available only when the endpoint isn't classified under the Create record action.
- Delete record action: Available only when the endpoint isn't classified under the Create record or Update record action.
- Search records action: Available only when the endpoint isn't classified under the Delete record, Create record, or Update record actions.
- Get record details by ID action: Available only when the endpoint isn't classified under the Delete record, Search records, Create record, or Update record action.
- Execute operation action: Available for endpoints not fitting into the Search records, Create record, Update record, Get record details by ID, or Delete record actions.
# Filtering API endpoints
This section instructs you on how to filter API endpoints effectively.
# List of rules
You can define rules to manage API endpoint visibility by configuring each rule to show or hide endpoints. This gives you control over which endpoints appear.
 View and manage your API endpoint filter rules
View and manage your API endpoint filter rules
# How to define a rule
To define filtering rules, fill in the following fields in Workato:
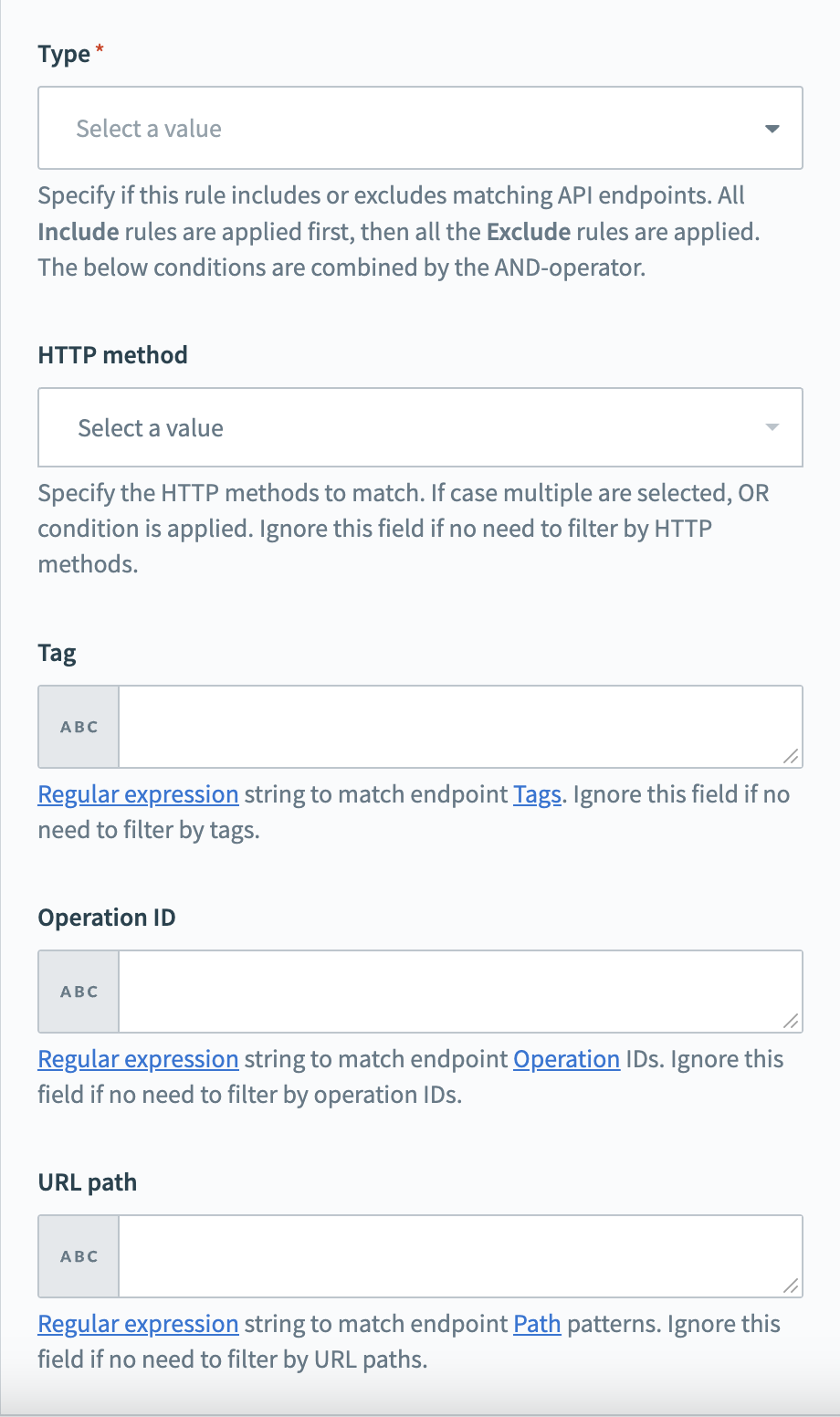 Define the specifics of your filtering rule
Define the specifics of your filtering rule
Choose to include or exclude endpoints in the Type field. Include rules are processed first, followed by exclude rules.
Choose HTTP methods (POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE) in the HTTP Method field to filter endpoints by operation type.
Enter regular expressions (opens new window) to match endpoint tags (opens new window) in the Tag field.
Enter regular expressions (opens new window) to match operation IDs (opens new window) in the Operation ID field.
Enter regular expressions (opens new window) to match URL paths (opens new window) in the URL Path field.
Ensure each endpoint meets all specified conditions for inclusion or exclusion. The system applies AND logic in rule processing.
# Configuration sample
{
...
"advanced" => {
"endpoint_filter_rules" => [
{
"type" => "include",
"operation_id" => "createPet"
},
...
]
}
...
}
# Ignoring action input fields
Actions in Workato contain input fields used to configure the action. Using the Ignore specific request fields field when setting up the connection, you can specify fields to ignore. Ignored input fields are hidden from view when users set up actions.
For example, let's say an endpoint contains a links field. Using the following configuration, this field can be ignored:
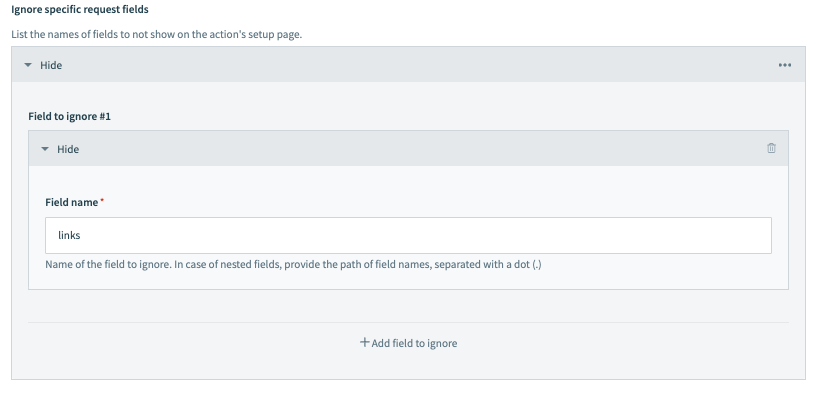
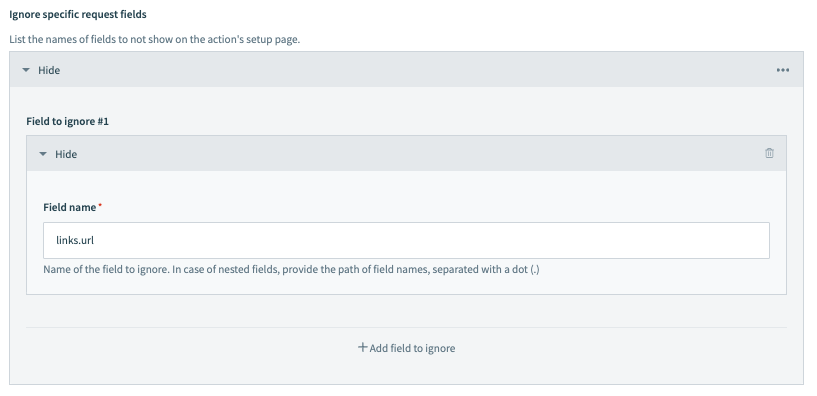
Nested fields can also be ignored by providing the field path using dot notation. For example, if links had a url field you wanted to ignore, you would enter links.url as the Field name:
# Customizing the application name
In the default source code, OpenAPI is used in several places. We recommend replacing this value with the name of your application when you create a custom connector.
CUSTOMIZE APPLICATION NAME FOR CUSTOM CONNECTORS
This section applies only to custom OpenAPI connectors.
Along with changing the application name, you can change other text elements to improve the user experience. For example, changing via to in.
Let's look at an example using the create_record action. In this case, OpenAPI is used in the action's subtitle:
create_record: {
title: 'Create record',
subtitle: 'Create record via OpenAPI',
description: lambda do |_input, picklist_label|
record = picklist_label['object_for_create'] || 'record'
"Create <span class='provider'>#{record}</span> " \
'via <span class="provider">OpenAPI</span>'
end,
[...]
Then in the recipe editor, the action will display like this:
Along with action subtitles, changing the application name to that of your application can affect several elements in the recipe editor, including:
Object field hints:
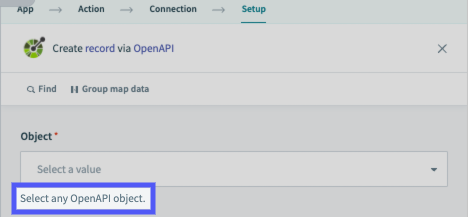
Recipe action descriptions:
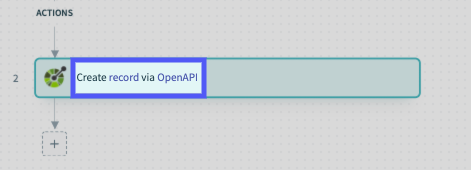
To simplify replacing OpenAPI with your application's name, perform a case-sensitive find/replace in the source code. Note: To perform this action, you may need to use a text editor like Sublime Text.
Last updated: 3/3/2026, 7:41:27 PM