# PostgreSQL - New row triggers
# New row
This trigger picks up rows that are inserted in the selected table or view. Each row is processed as a separate job. It checks for new rows once every poll interval.
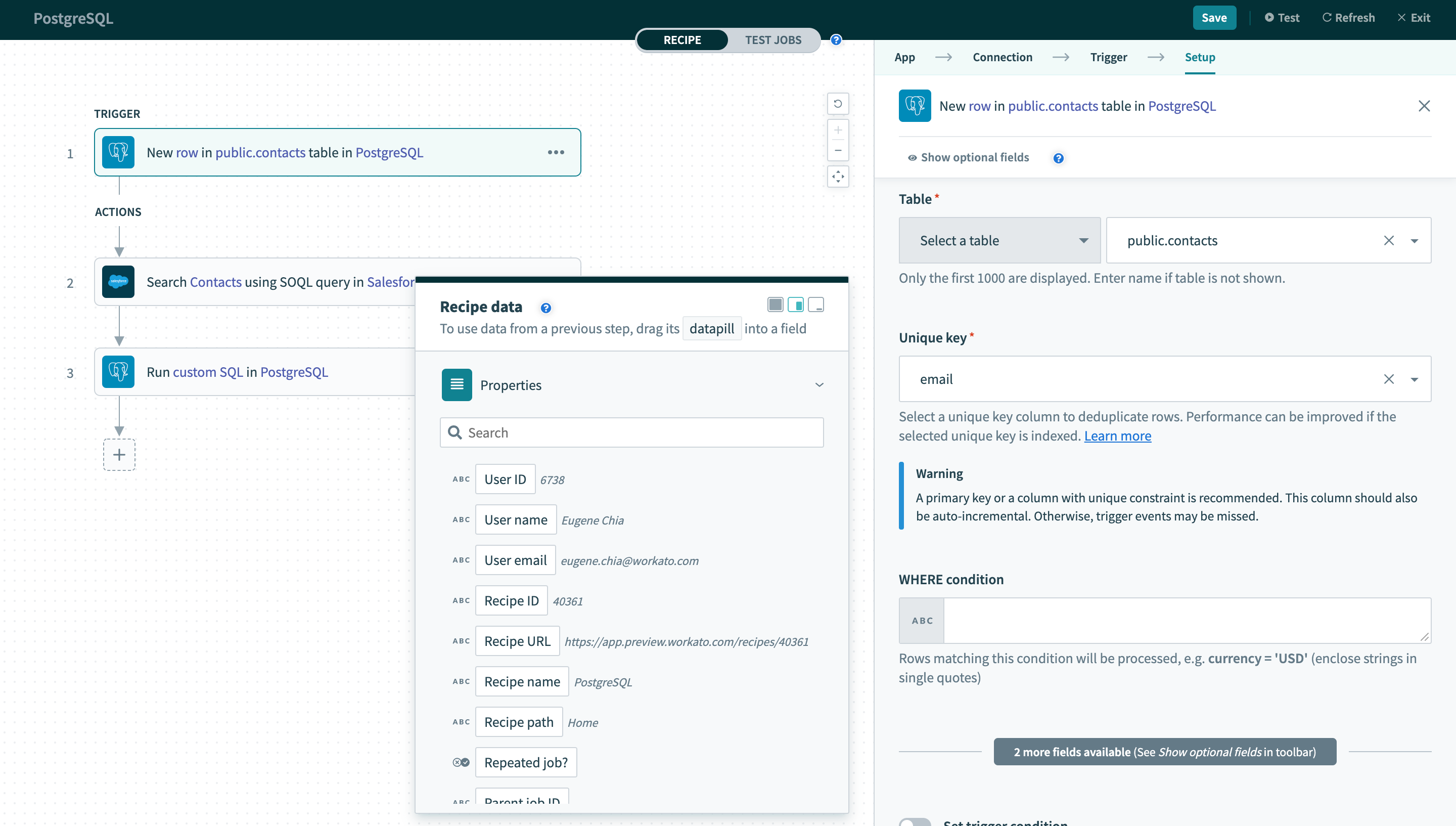 New row trigger
New row trigger
| Input field | Description |
|---|---|
| Table | First, select a table/view to process rows from. |
| Unique key | Next, select a unique key column to uniquely identify rows. This list of columns are generated from the selected table/view. |
| WHERE condition |
Finally, provide an optional WHERE condition to filter rows.
|
# New batch of rows
This trigger picks up rows that are inserted in the selected table or view. These rows are processed as a batch of rows for each job. This batch size can be configured in the trigger input. It checks for new rows once every poll interval.
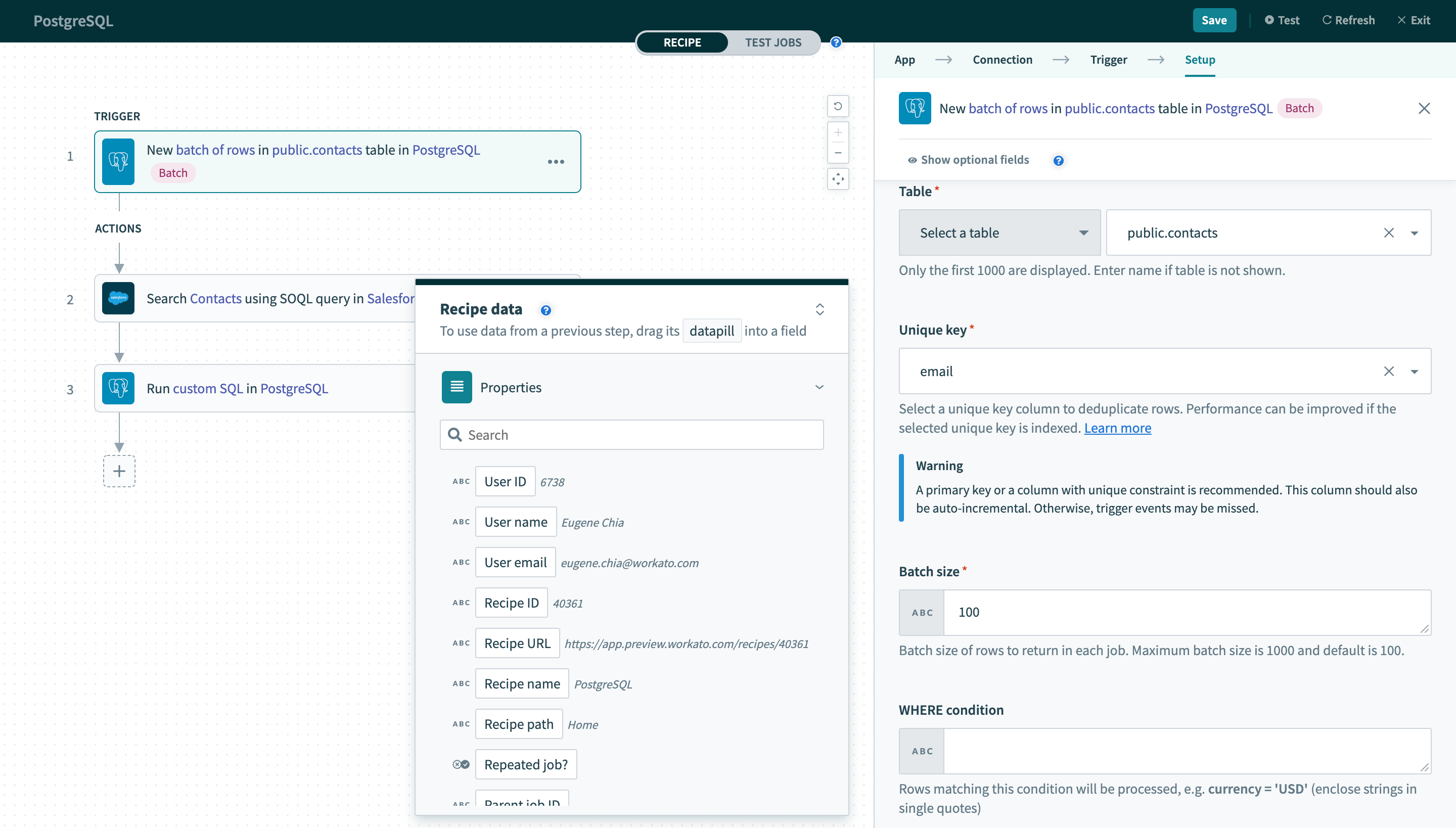 New batch of rows trigger
New batch of rows trigger
| Input field | Description |
|---|---|
| Table | First, select a table/view to process rows from. |
| Unique key | Next, select a unique key column to uniquely identify rows. This list of columns are generated from the selected table/view. |
| Batch size | Next, configure the batch size to process in each individual job for this recipe. |
| WHERE condition |
Finally, provide an optional WHERE condition to filter rows.
|
# Input
# Table
Select the table/view to process rows from. This can be done either by selecting a table from the pick list, or toggling the input field to text mode and typing the full table name.
# Unique key
Values from this selected column is used to deduplicate rows in the selected table, making sure that the same row is not processed twice in the same recipe.
As such, the values in the selected column should not be repeated in your table. Typically, this column is the primary key of the table (for example, ID). It should be incremental and sortable. This column can also be indexed for better performance.
Only columns that have PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE constraints can be used. Run this SQL query to find out which columns fulfill this requirement.
SELECT c.column_name
FROM information_schema.key_column_usage AS c
LEFT JOIN information_schema.table_constraints AS t
ON t.constraint_name = c.constraint_name
WHERE
t.table_schema = 'schema_name' AND
t.table_name = 'table_name' AND
t.constraint_type in ('PRIMARY KEY', 'UNIQUE')
ORDER BY c.ordinal_position;
# Batch size
Batch size of rows to return in each job. This can be any number between 1 and the maximum batch size. Maximum batch size is 100 and default is 100.
In any given poll, if there are less rows than the configured batch size, this trigger will deliver all rows as a smaller batch.
# WHERE condition
This condition is used to filter rows based on one or more column values.
status = 'closed' and priority > 3
Leave blank to process all rows from the selected table.
Complex WHERE conditions with subqueries can also be used. Refer to the WHERE condition guide for more information.
Last updated: 1/19/2026, 4:31:14 PM