# Use AWS Secrets Manager in connections
Video guide: Set up connections safely with AWS Secrets Manager
This guide explains how to use secrets from your Amazon Web Services (AWS) Secrets Manager vault to configure Workato connections.
# Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this guide, you must have the following prerequisites:
In Workato:
- A successful AWS Secrets Manager workspace-level or project-level connection.
- A user role with Create and Edit Connections privileges.
In Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- An existing secret in JSON key/value pair format. Workato doesn't support plaintext secrets. Refer to the AWS documentation for more information on how to create a secret (opens new window).
- Permissions that allow you to view secrets in AWS Secrets Manager.
# Retrieve the secret's details from AWS
Complete the following steps to retrieve the secret's details from AWS:
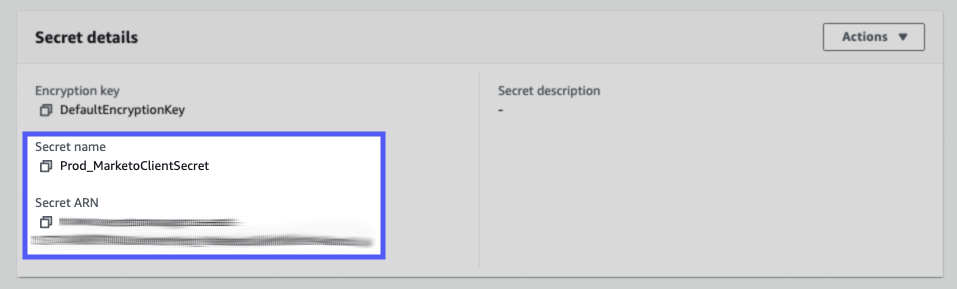
Sign in to your AWS Management Console and open the Secrets Manager console (opens new window).
In the navigation pane, click Secrets.
Click the secret you plan to use in Workato.
Copy and store the Secret name and Secret ARN securely. These values are required to configure the external secret in Workato.
# Configure a Workato connection
Complete the following steps to configure a connection in Workato using AWS Secrets Manager:
Create a new connection or open the configuration page for an existing connection in your Workato account.
Click or hover over the input field that requires an external secret, then click + Add external secret.
Enter the Key name and Secret ARN in the Add external secret dialog.
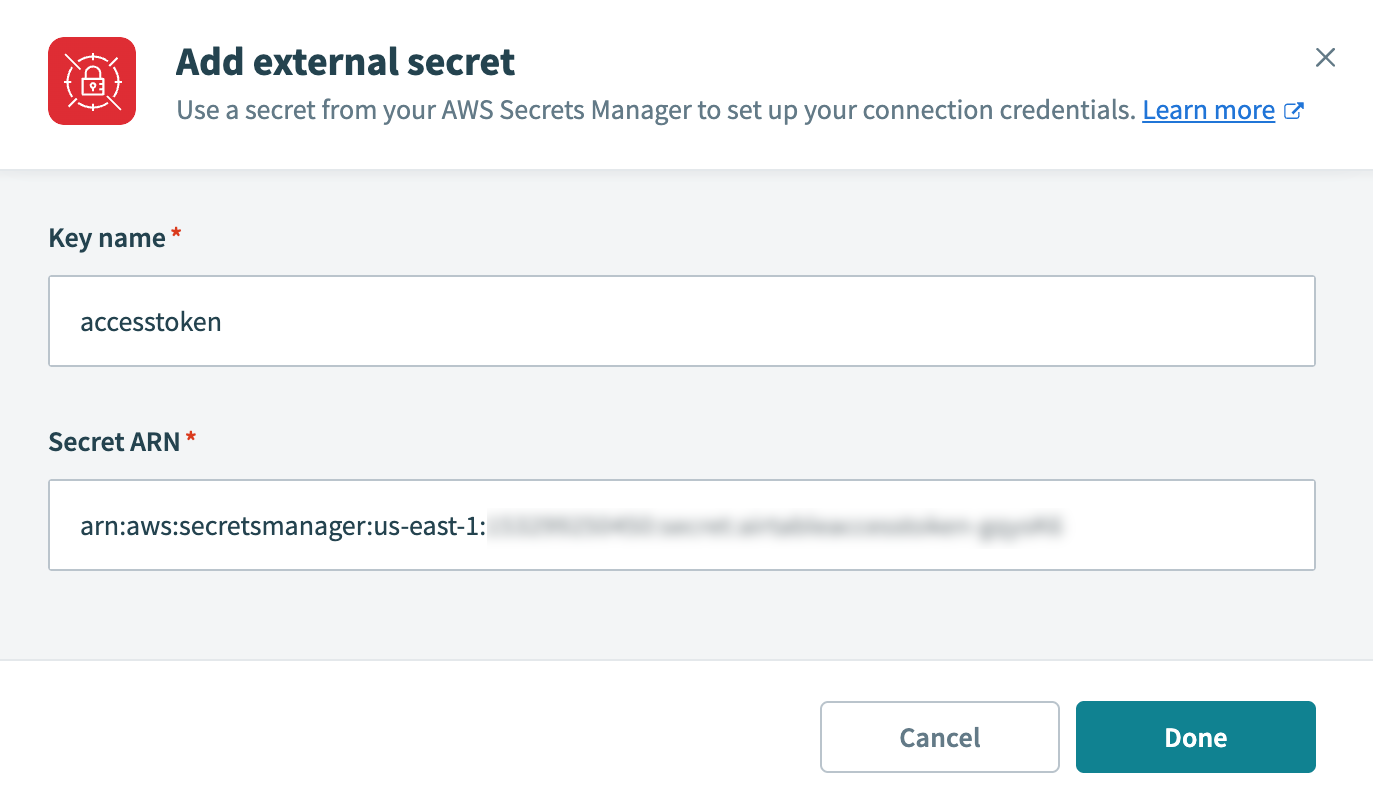 Add external secret
Add external secret
Click Done. The secret appears as a masked datapill in the input field on the connection page.
Select the datapill to edit the secret.
Click Connect and verify that this connection works.
If you prefer to add the secret with a secret mask, follow this syntax for the secrets used in Workato connection credentials:
{{workato:sm:<key name>:<secret ARN>}}
<key name>Refers to the specific key name within a secret, not the secret name itself. For example, in a secret named
jira, there may be a key/value pair whereprod.jira.secret.keyis the key name, and its value is the actual personal access token.<secret ARN>The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the secret in AWS Secrets Manager. For example:
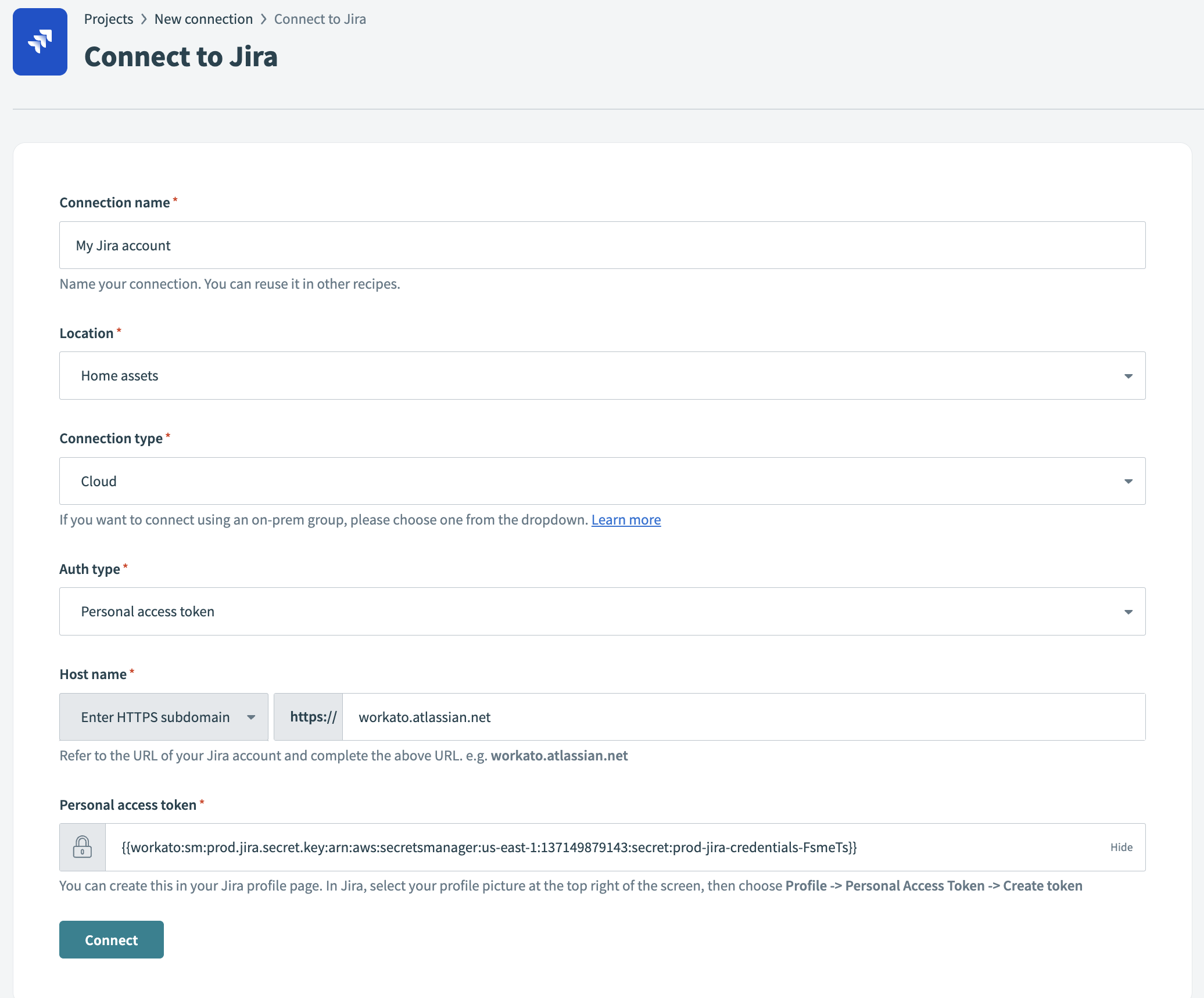
{{workato:sm:prod.jira.secret.key:arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:137149879143:secret:prod-jira-credentials-FsmeTs}}
In this example, prod.jira.secret.key is the key name in a secret named jira, and arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:137149879143:secret:prod-jira-credentials-FsmeTs is the secret ARN.
In the connection's configuration page, paste this entire value into the appropriate field. The following image shows a secret being used as the Custom Service client secret value in a Jira connection:
# Complete your connection setup
Select Connect to authorize and complete your connection setup.
# Secrets cache behavior
Workato caches credentials retrieved from AWS Secrets Manager for 60 minutes. During this period, recipes continue to use the cached value, even if you update or rotate the secret.
After the cache expires, the next recipe execution retrieves the latest value from AWS Secrets Manager. You can call the Clear secrets management cache endpoint to apply changes immediately. This forces Workato to fetch the latest credentials without requiring you to disconnect and reconnect the connection.
Last updated: 12/2/2025, 11:48:46 PM