# GitHub MCP server
The GitHub MCP server lets LLMs explore and manage information in GitHub repositories, issues, and pull requests. It provides AI assistants with tools to help users understand codebases, track development progress, monitor project health, and take action, such as create and update issues and pull requests, through natural conversation.
# Uses
Use the GitHub MCP server when you plan to perform the following actions:
- Explore repositories and understand project structure and activity
- Check the status of issues and pull requests
- Create new issues and pull requests
- Update existing issues and pull requests
- Add comments to issues for feedback and collaboration
- List available labels for consistent issue categorization
- Prepare for code reviews or development discussions
- Review recent commits and development changes
- Search across repositories for issues, pull requests, code, or projects
- Get situational awareness of development activity or personal workload
- Request reviewers and manage pull request metadata
# Example prompts
What's the status of the authentication-service repo?Give me a development summary for our platform repositoryWhat's been happening in the api-gateway repo this week?How active is the mobile-app repository? Any open PRs?Summarize recent activity in acme-corp/backend-servicesCreate a bug report for the login timeout issue in the backend-api repoUpdate issue #234 to high priority and assign it to SarahAdd a comment to issue #456 with the latest test resultsCreate a pull request from feature/new-auth to mainAdd reviewers to PR #789 and mark it ready for reviewWhat labels are available in the mobile-app repository?
# GitHub MCP server tools
The GitHub MCP server provides the following tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| get_issue | Retrieves detailed information about a specific GitHub issue, including its full description and comments. |
| get_pull_request | Retrieves detailed information about a specific pull request, including changes, reviews, and discussion. |
| get_repository | Retrieves repository metadata, including name, description, visibility, default branch, primary language, star/fork counts, and recent activity indicators. |
| get_user_context | Retrieves information about a GitHub user or organization, including their repositories and activity. |
| list_commits | Retrieves recent commit history for a repository or specific branch. |
| list_file_changes | Retrieves a list of file changes in a specified pull request. |
| list_review_comments | Retrieves all review comments for a specified pull request. |
| list_reviews | Retrieves a list of all reviews for a specified pull request. |
| search_code | Searches for specific keywords, functions, or snippets within code files across GitHub. |
| search_issues | Retrieves a list of issues. |
| search_pull_requests | Retrieves a list of pull requests. |
| search_repositories | Retrieves a list of repositories. |
| add_issue_comment | Adds a comment to an existing GitHub issue. |
| create_issue | Creates a new issue in a GitHub repository with the title, description, labels, and assignees you specify. |
| create_pull_request | Creates a new pull request in a GitHub repository using the head and base branches you specify. |
| list_labels | Retrieves all labels available in a repository. |
| update_issue | Updates an existing issue's state, labels, assignees, or milestone. |
| update_pull_request | Updates an existing pull request including reviewers, labels, or draft status. |
# Install the GitHub MCP server
Complete the following steps to install a prebuilt MCP server to your project:
Sign in to your Workato account.
Go to AI Hub > MCP servers.
Click + Create MCP server.
Go to the Start with a template section and select the prebuilt MCP server you plan to use.
Click Use this template.
Provide a name for your MCP server in the MCP server name field.
Go to the Connections section and connect to your app account.
Select the connection type you plan to use for the MCP server template.
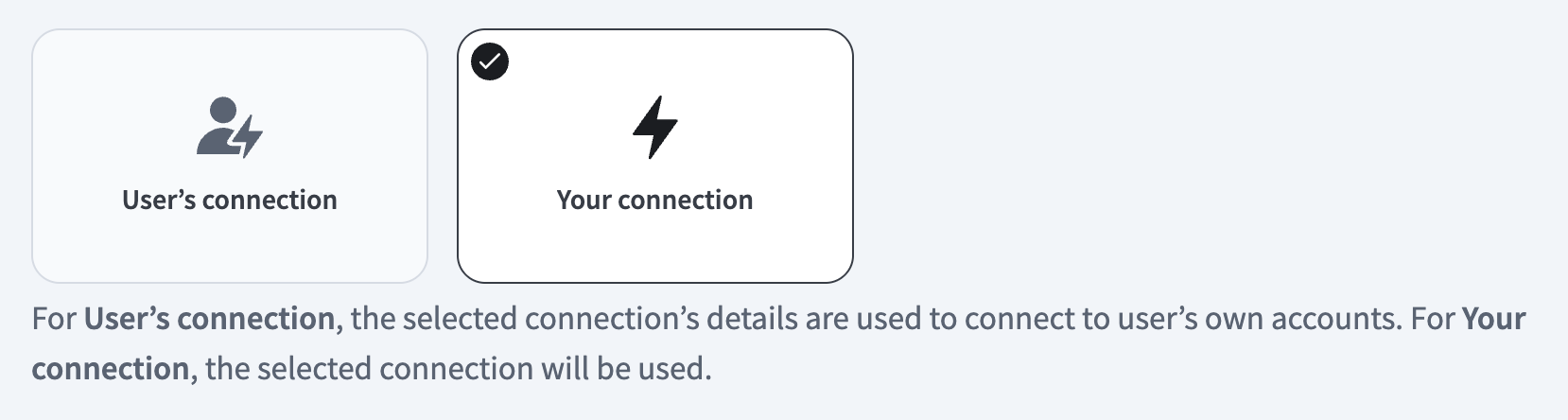
- User's connection: MCP server tools perform actions based on the identity and permissions of the user who connects to the application. Users authenticate with their own credentials to execute the skill.
- Your connection: This option uses the connection established by the recipe builder and follows the same principles as normal app connections.
 Select your connection type
Select your connection type
VERIFIED USER ACCESS AUTHENTICATION REQUIREMENTS
Only app connections that use OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant are available for user's connection. Refer to Verified user access for more information.
Complete the app-specific connection setup steps in the following section.
# GitHub connection setup
Connect to GitHub on Workato using one of the following authentication methods:
- OAuth authentication. Workato recipes act on your behalf.
- GitHub Apps. Workato recipes act as the app. Refer to GitHub App authentication .
- A personal access token
Refer to the GitHub documentation (opens new window) for more information.
# OAuth authentication
View OAuth authentication steps
Complete the following steps to connect your GitHub to Workato using OAuth authentication:
Sign in to your Workato account and go to the project where you plan to add your GitHub connection.
Click Create > Connection, then select GitHub as your connection.
Provide a Connection name that identifies which GitHub instance Workato is connected to.
Use the Location drop-down menu to select the project where you plan to store the connection.
Use the Authentication type drop-down menu and select OAuth App.
Optional. Click Advanced configuration to display the Host name field.
Optional. Enter a Host name. This is applicable when using Github Enterprise Server. Enter your Github subdomain. For example, if your host URL is https://github.example-organisation.com, the subdomain is github.example-organisation.com.
Click Connect. Workato redirects you to GitHub. The OAuth App requests authorization to act on your behalf. Workato performs actions such as creating comments, issues, and pull requests under your GitHub user.
# GitHub App authentication
You must first register the app in your GitHub account and retrieve the credentials to connect to GitHub using a GitHub App.
 Select Authentication type as GitHub app and collect details from your GitHub App!
Select Authentication type as GitHub app and collect details from your GitHub App!
# Register your GitHub app
View step to register your GitHub App
Complete the following steps to register your GitHub App and retrieve the credentials required to connect it to Workato:
Complete the steps (opens new window) in the GitHub documentation to register your GitHub App.
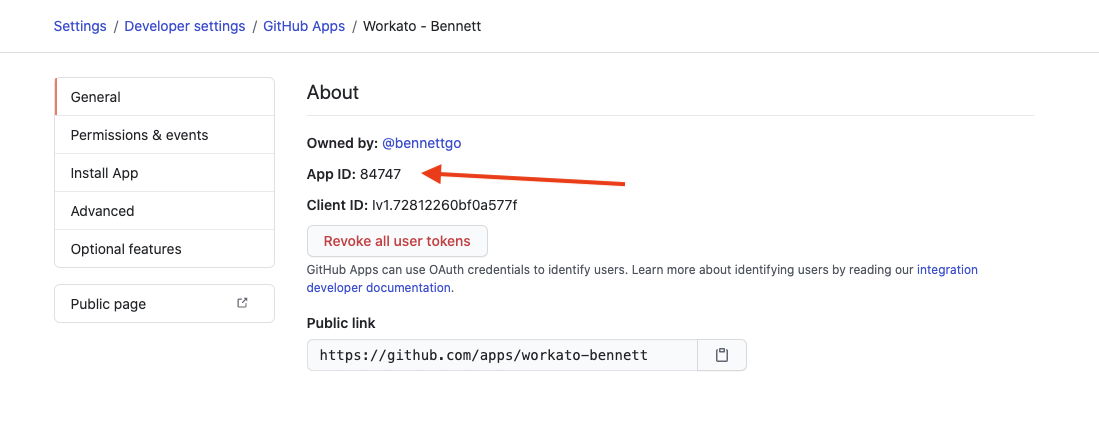
Retrieve your GitHub App ID in the General settings page of your GitHub app.
 Save this App ID and place it into your connection
Save this App ID and place it into your connection
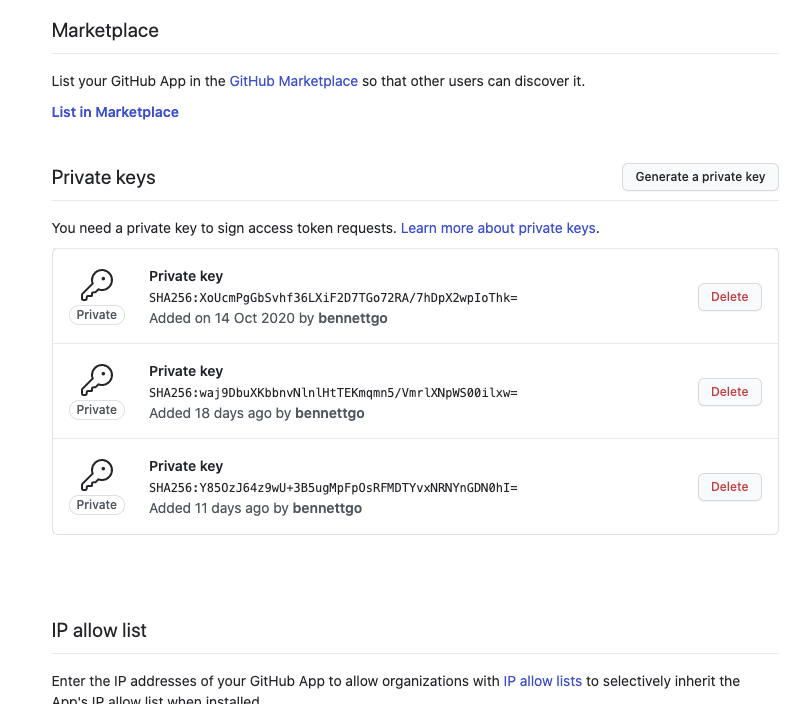
Generate a Private key on the same page. GitHub automatically downloads this .pem file to your machine.
 Generate the private key
Generate the private key
Open the .pem file in a text editor. The file should look similar to the following:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIEpAIBAAKCAQEAyL/wuiSaWoH0pyf366G5E7dbzzmON1qMMrWvls8RtZtgOLjb
FBxj6gO2aUfoGbMCMqOYRV6xCn6tK118sGYMd5U/kCFu3IRPr/2GoEtcrf0TecQG
ON+27ijH0Vpn62o8NzGejdy0AWujrtAl6F8xGZeze0PzrGvW6h/GnAdZO1gJnp8t
wmEqEMXqAsPOQ0hkY+r+pE8RKQVsJCe+PIanBKp7RKWDi9usPFZQdQ==
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
Copy the entire private key, including the -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- and -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----. Use this private key when you set up the connection in Workato.
Retrieve your Installation ID from the organization or user where you installed your GitHub App:
- Users accounts: Go to Settings > Applications > Your GitHub App > Configure.
- Organizations: Go to your organization's GitHub homepage. Click Settings > Installed GitHub Apps > Configure.
The installation ID appears in the URL. For example, if the URL is https://github.com/settings/installations/13876669, the installation ID is 13876669.
Save the installation ID. Enter this ID when creating the GitHub App connection in Workato.
# Configure GitHub app authentication
View steps to authenticate your GitHub app
Provide a Connection name that identifies which GitHub instance Workato is connected to.
Use the Location drop-down menu to select the project where you plan to store the connection.
Use the Authentication type drop-down menu and select GitHub App.
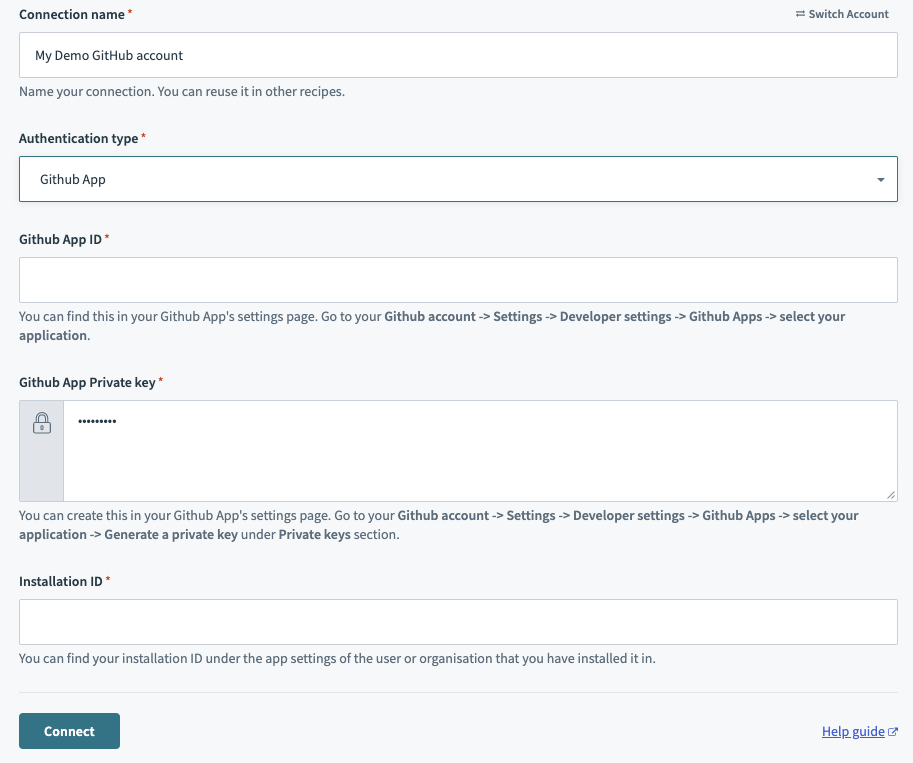
Enter your GitHub App ID.
Enter your Github App Private key.
Enter your Installation ID.
Optional. Click Advanced configuration to display the Host name field.
Optional. Enter a Host name if using GitHub Enterprise Server. Use your GitHub subdomain. For example, if your host URL is https://github.example-organisation.com, the subdomain is github.example-organisation.com.
Optional. Enter a Custom OAuth profile. This selection ensures that all requests to the app use the specified profile.
Click Connect.
# Personal access token authentication
Retrieve your personal access token from GitHub to connect your GitHub account to Workato using a personal access token:
View steps to retrieve your GitHub personal access token
Go to Github account > Settings > Developer settings > Personal access tokens > Generate new token.
Click Generate new token.
Copy the token. Enter this token in Workato to authenticate the connection.
# Complete setup in Workato
View Complete setup in Workato steps
Complete the following steps to set up your GitHub connection using a personal access token:
Sign in to your Workato account and go to the project where you plan to add your GitHub connection.
Click Create > Connection, then select GitHub as your connection.
Provide a Connection name that identifies which GitHub instance Workato is connected to.
Use the Location drop-down menu to select the project where you plan to store the connection.
Use the Authentication type drop-down menu and select Personal Access Token.
Optional. Click Advanced configuration to display the Host name field.
Optional. Enter a Host name. This is applicable when using Github Enterprise Server. Enter your Github subdomain. For example, if your host URL is https://github.example-organisation.com, your subdomain is github.example-organisation.com.
Enter your Personal Access Token.
Optional. Enter a Custom OAuth profile. This ensures all requests to the app use the specified profile.
Click Connect.
# How to use GitHub MCP server tools
Refer to the following sections for detailed information on available tools:
# get_issue tool
The get_issue tool retrieves the full details of a GitHub issue, including the description, labels, assignees, and the most recent discussion history. Your LLM uses this tool to understand the requirements of a task, check the status of a bug, or catch up on the latest feedback in an issue's comments.
Try asking:
What is the current status of issue #452 and who is assigned to it?Summarize the last few comments on the 'login page bug' issue.Give me the full description and any linked pull requests for the 'API migration' task.Read the 'database performance' issue and tell me what labels have been applied.
# get_pull_request tool
The get_pull_request tool retrieves the complete details of a pull request, including its description, merge status, and a summary of the code changes. Your LLM uses this tool to review progress on a feature, see which files were modified, or understand the relationship between code changes and linked issues.
Try asking:
What’s the status of PR #82 and is it currently mergeable?Summarize the changes in the 'add-auth-layer' pull request.Which files were modified in the latest PR from @Sarah?Check the 'fix-header-styling' PR and tell me which issues it's intended to close.
# get_repository tool
The get_repository tool retrieves the high-level details and metadata for a specific repository, including its purpose, primary language, and current activity stats. Your LLM uses this tool to get an overview of a project, read its documentation, such as README files, or check the number of open issues and pull requests to gauge the project's health.
Try asking:
Get the details for the 'workato-mcp-server' repository.Show me the README and general info for the 'frontend-ui' repoWhat is the primary language and star count for the 'analytics-engine' project?Give me an overview of the repository at https://github.com/org/<example>.
# get_user_context tool
The get_user_context tool retrieves profile information for GitHub users and organizations. Your LLM uses this tool to learn more about a contributor’s background, view an organization's public portfolio, or identify the most popular repositories owned by a specific user or team.
Try asking:
Who is @octocat and what are their most popular repositories?Get the profile information and public repo count for the 'Workato' organization.Show me the bio and location for the user who opened the latest pull request.Find out which company @janderson is associated with and list their recent projects.
# list_commits tool
The list_commits tool retrieves the history of changes made to a repository. Your LLM uses this tool to track recent development activity, find out who made specific changes, or audit the progress of a project over a certain period of time.
Try asking:
What are the last 10 commits made to the 'main-site' repository?Show me the recent commit history for @Sarah in the 'backend-api' repo.What changes were committed to the 'production' branch in the last 48 hours?List the commits from last week to see the progress on the 'auth-feature' branch.
# list_file_changes tool
The list_file_changes tool retrieves a list of all files that were modified, added, or deleted within a specific pull request. Use this tool to see the scope of a code review, identify which parts of the system are being impacted, or verify that the correct files were included in a change set.
Try asking:
Which files were changed in pull request #105?List the files modified in the 'fix-navigation-bug' PR.Show me a list of all files impacted by the latest changes in the 'mobile-app' repo.Check PR #202 to see if any configuration files were updated.
# list_review_comments tool
The list_review_comments tool retrieves all comments made during the code review process of a specific pull request. Your LLM uses this tool to see feedback from reviewers, track open questions about code implementation, or verify if requested changes have been addressed.
Try asking:
Show me all the review comments on pull request #82.What feedback did the reviewers provide on the 'api-refactor' PR?List the code review comments for the latest changes in the 'mobile-app' repo.Read the review discussion on PR #150 to see if there are any unresolved issues.
# list_reviews tool
The list_reviews tool retrieves a summary of all formal reviews submitted for a specific pull request, including the reviewer’s name, the state of the review, such as Approved, Changes Requested, or Commented, and the submission time. Your LLM uses this tool to check if a pull request has received the necessary approvals or to see which team members have already weighed in.
Try asking:
Has anyone approved pull request #82 yet?Show me all the reviews for the 'database-patch' PR to see if changes were requested.List the review status for PR #210 to see who still needs to sign off.Check the review history for the latest pull request in the 'security-updates' repo.
# search_code tool
The search_code tool searches for specific keywords, functions, or snippets within code files across GitHub. Your LLM uses this tool to find where a specific function is defined, locate examples of how a library is used, or find every instance of a hardcoded string across your repositories.
Try asking:
Search for any code containing the 'calculate_tax' function across all repos.Find examples of how we use the 'acme-api' library in our codebase.Search for the string 'DEPRECATED' in the 'legacy-app' repository.Look for where the 'EnvironmentConfig' class is defined in our TypeScript files.
# search_issues tool
The search_issues tool retrieves a list of issues from your repositories based on keywords, status, or labels. Your LLM uses this tool to track down bug reports, check the progress of specific feature requests, or see what tasks are currently open or closed across your project.
Try asking:
Find all open issues related to 'performance' in the 'backend' repo.Search for any closed issues about 'login' to see how they were resolved.What are the most recent high-priority issues across our organization?Look for issues labeled 'documentation' that are currently assigned to @Sarah.
# search_pull_requests tool
The search_pull_requests tool retrieves pull requests based on keywords, status, or reviewers. Your LLM uses this tool to stay on top of your development pipeline, find recently merged work, or identify which code changes are still waiting for approval.
Try asking:
Find all open pull requests that are waiting for a review.Search for recently merged PRs related to 'ui-updates'.What pull requests are currently open in the 'mobile-app' repository?Show me all closed pull requests created by @James in the last month.
# search_repositories tool
The search_repositories tool retrieves a list of GitHub repositories based on names, descriptions, or topics. Your LLM uses this tool to locate specific projects, discover repositories related to a particular technology, or find the correct repository name before you perform more detailed actions like checking issues or code.
Try asking:
Find all repositories related to 'machine-learning' in our organization.Search for a repository named 'customer-portal'.What public repositories does @workato have for 'mcp-servers'?Look for repositories that use 'React' and have 'dashboard' in the name.
# add_issue_comment tool
The add_issue_comment tool adds a comment to an existing GitHub issue. Your LLM uses this tool to provide status updates, answer questions, share additional context, or document decisions directly in the issue thread without leaving your conversation.
Try asking:
Add a comment to issue #342 saying we've completed the database migration.Comment on the 'login timeout' issue that we're investigating the root cause.Post an update to issue #789 with the latest performance test results.Add a note to the authentication bug explaining the workaround we found.
# create_issue tool
The create_issue tool creates a new issue in a GitHub repository with the title, description, labels, and assignees you specify. Your LLM uses this tool to capture bugs, feature requests, or tasks from your conversation and immediately create properly formatted, actionable issues without manual data entry.
Try asking:
Create a bug report in 'backend-api' for the timeout issue I just described.Open a new feature request for dark mode support in the 'mobile-app' repo.File an issue about the broken payment flow and assign it to @Sarah.Create a high-priority task for updating our SSL certificates, labeled 'security'.
# create_pull_request tool
The create_pull_request tool creates a new pull request in a GitHub repository using the head and base branches you specify. Your LLM uses this tool to initiate code reviews, propose changes from a feature branch, or open a PR with a pre-filled description based on your conversation context.
Try asking:
Create a pull request from 'feature/new-auth' to 'main' for the authentication updates.Open a PR merging 'bugfix/timeout-issue' into 'develop' with a summary of the changes.Create a pull request for the UI redesign branch targeting 'staging'.Open a PR from my 'docs-update' branch and request a review from @James.
# list_labels tool
The list_labels tool retrieves all labels available in a repository. Your LLM uses this tool to discover which labels exist before creating or updating issues, ensure consistent labeling across your project, or help you find the correct label name when filtering issues.
Try asking:
What labels are available in the 'backend-services' repository?Show me all the labels we use in the 'mobile-app' repo.List the priority and status labels for our 'customer-portal' project.What bug tracking labels do we have set up in this repository?
# update_issue tool
The update_issue tool updates an existing issue's state, labels, assignees, or milestone. Your LLM uses this tool to change an issue's status as work progresses, reassign tasks, update priority levels, or modify any issue field based on your conversation without navigating to GitHub.
Try asking:
Close issue #456 and add a comment that it's been resolved.Change the priority of issue #234 to 'high' and assign it to @Maria.Update the authentication bug to 'in-progress' status.Add the 'needs-review' label to issue #789 and remove 'blocked'.
# update_pull_request tool
The update_pull_request tool updates an existing pull request including reviewers, labels, or draft status. Your LLM uses this tool to request additional code reviews, mark a PR as ready for review, update labels to reflect the current state, or modify PR metadata as your development workflow progresses.
Try asking:
Add @Sarah and @James as reviewers to PR #567.Mark pull request #890 as ready for review and remove draft status.Update PR #234 with the 'needs-testing' label.Request a review from the frontend team on the UI redesign pull request.
# Getting started
View and manage your MCP server tools in the Overview page Tools section. Tool management provides the following capabilities:
TOOLS MUST BE STARTED
Your LLM can only access active tools in your MCP server connector.
Last updated: 3/5/2026, 12:08:37 AM